A dead car battery can be a frustrating experience, often leaving you stranded. Fortunately, jump-starting your car with jumper cables is a straightforward solution that can get you back on the road quickly. This guide provides a detailed, step-by-step process on how to safely and effectively jump-start your car using jumper cables and another vehicle.
Before you begin, it’s crucial to understand the process and take necessary safety precautions. Jump-starting involves connecting your car battery to a functioning battery in another vehicle to provide the electrical boost needed to start your engine.
To jump-start your car safely and efficiently, follow these steps:
-
Gather Your Equipment: Jumper Cables
The first thing you’ll need is a set of jumper cables. It’s wise to keep a set in your car’s trunk for emergencies. If you don’t have any, you’ll need to find a helpful person with a working vehicle who also has jumper cables. Ensure the jumper cables are in good condition, without any frayed wires or damaged clamps.
-
Position the Vehicles Safely
Carefully position the working car so that it’s facing your car, or parked close enough that the jumper cables can reach both batteries. Make sure both vehicles are in Park (P) or Neutral (N) for manual transmissions, and that both ignitions are turned off completely. Engage the parking brakes in both cars to prevent any accidental movement.
-
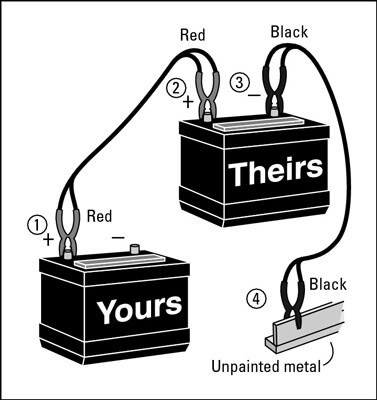
Locate the Positive Terminals and Connect the First Red Clip
On your dead car battery, identify the positive (+) terminal. It’s usually marked with “POS” or “+” and is often covered with a red cap. Attach one of the red jumper cable clips to this positive terminal. Ensure you have a firm grip and a good connection.
-
Connect the Second Red Clip to the Working Car’s Positive Terminal
Now, go to the working car and locate its positive (+) battery terminal. Attach the other red jumper cable clip to this positive terminal, again ensuring a secure connection.
-
Connect the First Black Clip to the Working Car’s Negative Terminal
Next, take one of the black jumper cable clips and connect it to the negative (-) terminal of the working car’s battery. The negative terminal is usually marked with “NEG” or “-” and might have a black cap.
-
Ground the Circuit: Connect the Last Black Clip to a Metal Part of Your Car
This is a crucial safety step. Do not connect the remaining black clip to the negative terminal of your dead battery. Instead, attach it to an unpainted metal surface on your car, away from the battery. Good grounding points include a metal strut that supports the hood or any other clean, unpainted metal part of the engine block. This grounding minimizes the risk of sparks igniting battery gases.
-
Start the Working Vehicle and Let it Run
Start the engine of the working vehicle and let it run for a few minutes. This allows the working car’s alternator to send charge to your dead battery. Allowing it to run for about 5 minutes can provide a good initial charge.
-
Attempt to Start Your Car
Now, try to start your car. Turn the ignition key and see if your engine starts. If it starts, congratulations! Let your engine run and proceed to the next step.
If your car doesn’t start immediately, ensure all cable connections are tight and secure. Have the person in the working car rev their engine slightly for a few minutes to provide a stronger charge. Then, try starting your car again. If it still doesn’t start after a few attempts, your battery might be beyond jump-starting and may need replacement, or there could be another issue preventing your car from starting.
-
Disconnect the Jumper Cables in Reverse Order
Once your car has started, carefully disconnect the jumper cables in the reverse order of connection to avoid sparks and potential electrical issues:
a. Remove the black clip from the unpainted metal surface of your car.
b. Remove the black clip from the negative terminal of the working car’s battery.
c. Remove the red clip from the positive terminal of the working car’s battery.
d. Remove the red clip from the positive terminal of your car’s battery. -
Keep Your Engine Running to Recharge
After a successful jump start, do not immediately turn off your engine. Drive your car around for at least 15-20 minutes to allow your car’s alternator to recharge the battery. If your car fails to start the next time you try to use it, it’s a strong indication that your battery is no longer holding a charge and likely needs to be replaced.
Important Considerations:
- Battery Voltage: Ensure the working vehicle has a battery with at least the same voltage as your car’s battery (usually 12V for most cars).
- Electronic Ignition and Alternative Fuel Vehicles: If either vehicle has an electronic ignition system or is an alternatively fueled vehicle, consult your owner’s manual or a professional before attempting to jump-start, as it may cause damage.
- Safety First: Always wear safety glasses and gloves if possible when working with car batteries. Avoid smoking or open flames near the battery.
What If Jump Starting Doesn’t Work?
If your car fails to jump-start even after following these steps, it could indicate a more serious problem. Potential issues include:
- Severely Damaged Battery: The battery might be too old or damaged to hold a charge, even with a jump start.
- Alternator Problems: If your alternator is faulty, it might not be charging your battery while driving, leading to repeated battery drain.
- Starter Motor Issues: A problem with the starter motor itself could prevent the car from starting, even with a fully charged battery.
- Other Electrical Issues: Fuses, wiring problems, or other electrical component failures could also be the cause.
In such cases, it’s best to seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic to diagnose and fix the underlying issue.
Jump-starting a car is a valuable skill for any driver. By following these steps carefully, you can safely jump-start your car and get back on the road. However, remember that jump-starting is often a temporary solution. If you experience repeated dead battery issues, it’s essential to have your battery and charging system inspected to prevent future breakdowns.