Your car alternator is a vital component that keeps your battery charged and your electrical system running smoothly. When it fails, your car will eventually stop running, leaving you stranded. Luckily, understanding the signs of a failing alternator and being able to diagnose the problem can save you a lot of headaches and potential breakdowns.
Signs of a Failing Alternator
There are a few telltale signs that your car alternator may be on its way out. Pay attention to these symptoms, as they could be early indicators of a serious issue:
- Dim headlights: If your headlights are noticeably dimmer than usual, especially when you turn on the air conditioning or other electrical accessories, this could be a sign that your alternator isn’t producing enough power.
- Battery light on the dashboard: A warning light on your dashboard is a clear indication that something is wrong. If the battery light comes on, it often means your alternator is failing to charge the battery properly.
- Strange noises coming from the engine: An alternator can make a whining, grinding, or squealing noise, especially when the engine is running.
- Electrical problems: If you experience other electrical issues, such as flickering lights, slow-starting windows, or malfunctioning power accessories, it could be due to a failing alternator.
- Dead battery: If you find yourself struggling to start your car, or your battery keeps dying, it’s a good idea to have your alternator checked. A faulty alternator can’t charge your battery, which can lead to a dead battery.
How to Diagnose Car Alternator Problems
Diagnosing alternator problems can be done with some simple tests and observations. Here are some steps you can follow:
- Check the battery terminals: Make sure the battery terminals are clean and secure. Loose or corroded terminals can prevent the alternator from properly charging the battery.
- Inspect the alternator belt: Visually inspect the alternator belt for signs of wear, cracks, or fraying. A worn belt can slip and prevent the alternator from spinning, leading to charging problems.
- Check the alternator wiring: Inspect the wiring connected to the alternator for any loose connections, frayed wires, or signs of damage.
- Use a multimeter: A multimeter is a valuable tool for testing the output voltage of the alternator. With the engine running, you can measure the voltage at the battery terminals. If the voltage is significantly lower than 13.5 volts, it indicates that the alternator is not charging properly.
- Listen for strange noises: Pay attention to any unusual sounds coming from the engine, particularly when the engine is running. A whining, grinding, or squealing noise could be a sign of a faulty alternator bearing.
- Perform a load test: You can perform a load test on the alternator using a special tool or by putting a heavy electrical load on the system (like turning on headlights and air conditioning) while measuring the voltage at the battery terminals. If the voltage drops significantly, it suggests a problem with the alternator.
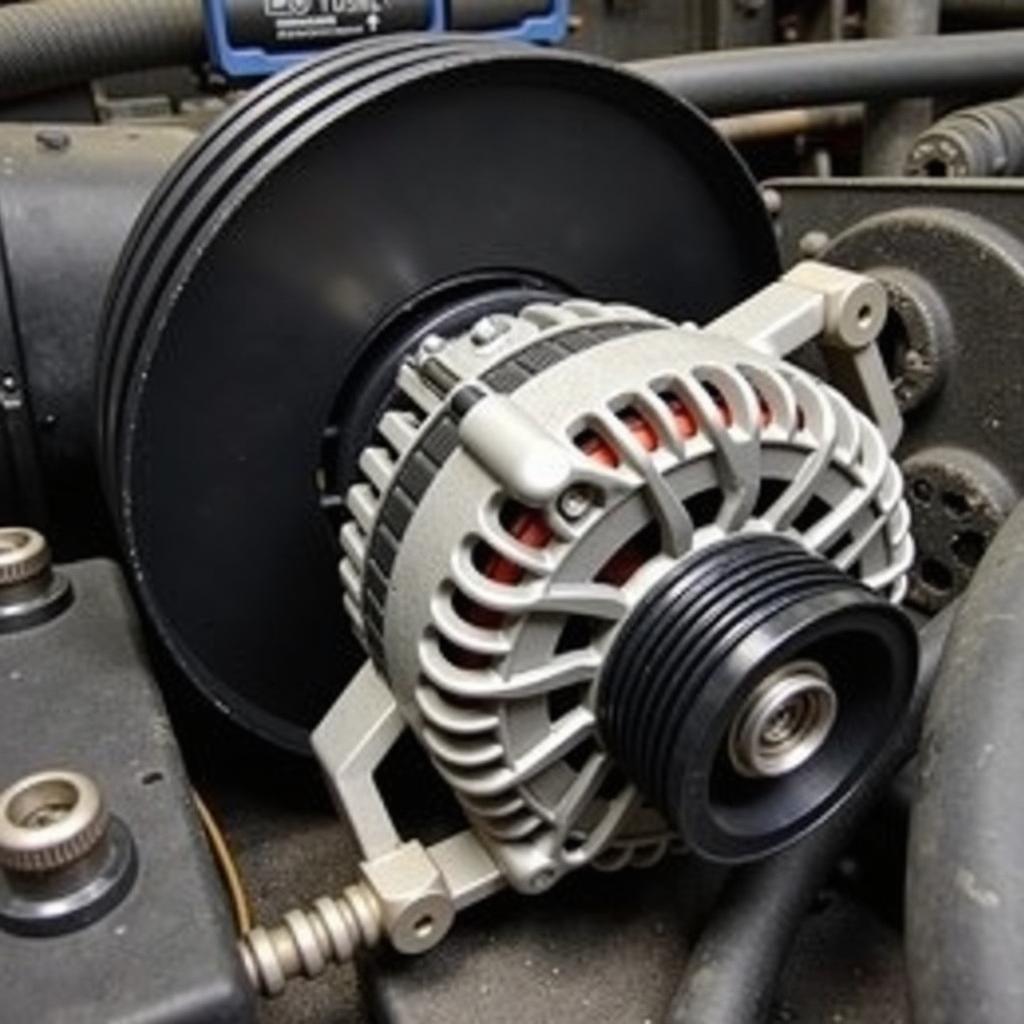 Inspecting the Alternator Belt
Inspecting the Alternator Belt
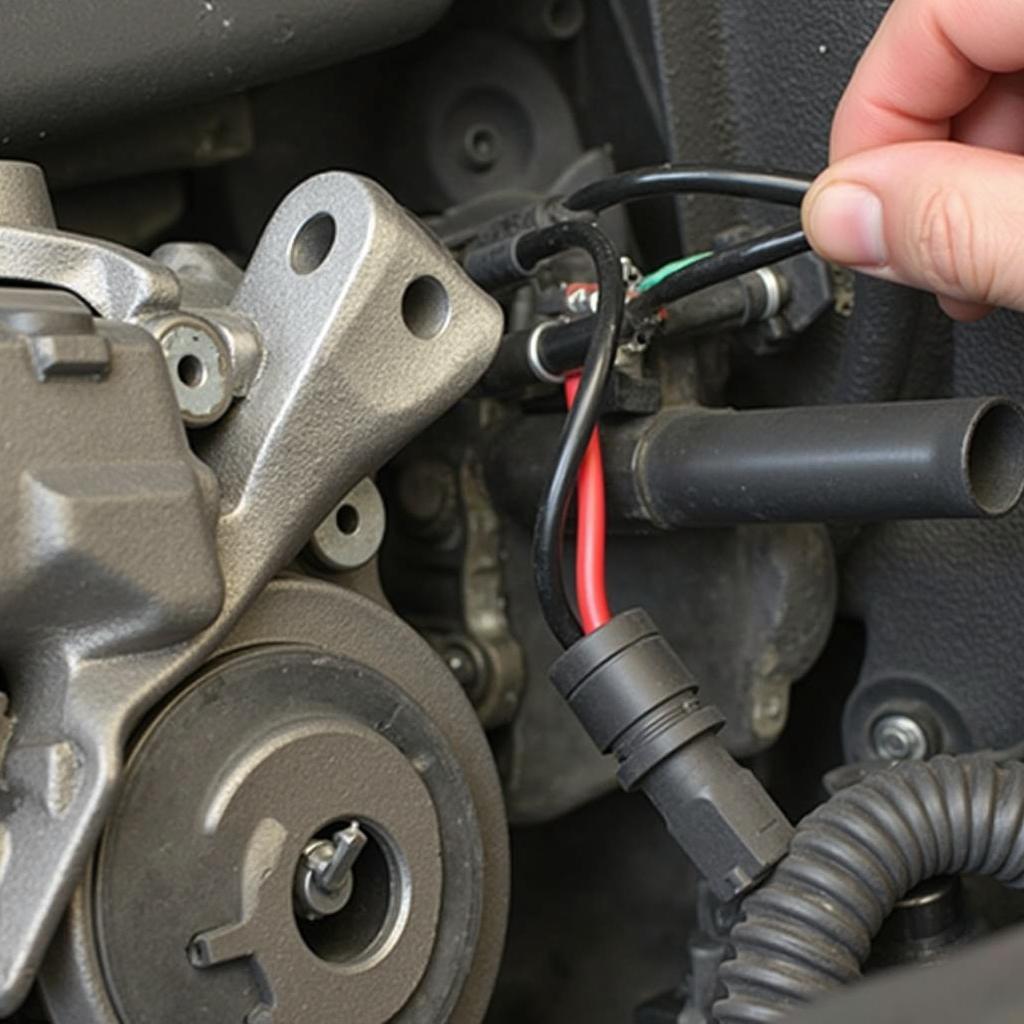 Inspecting the Alternator Wiring
Inspecting the Alternator Wiring
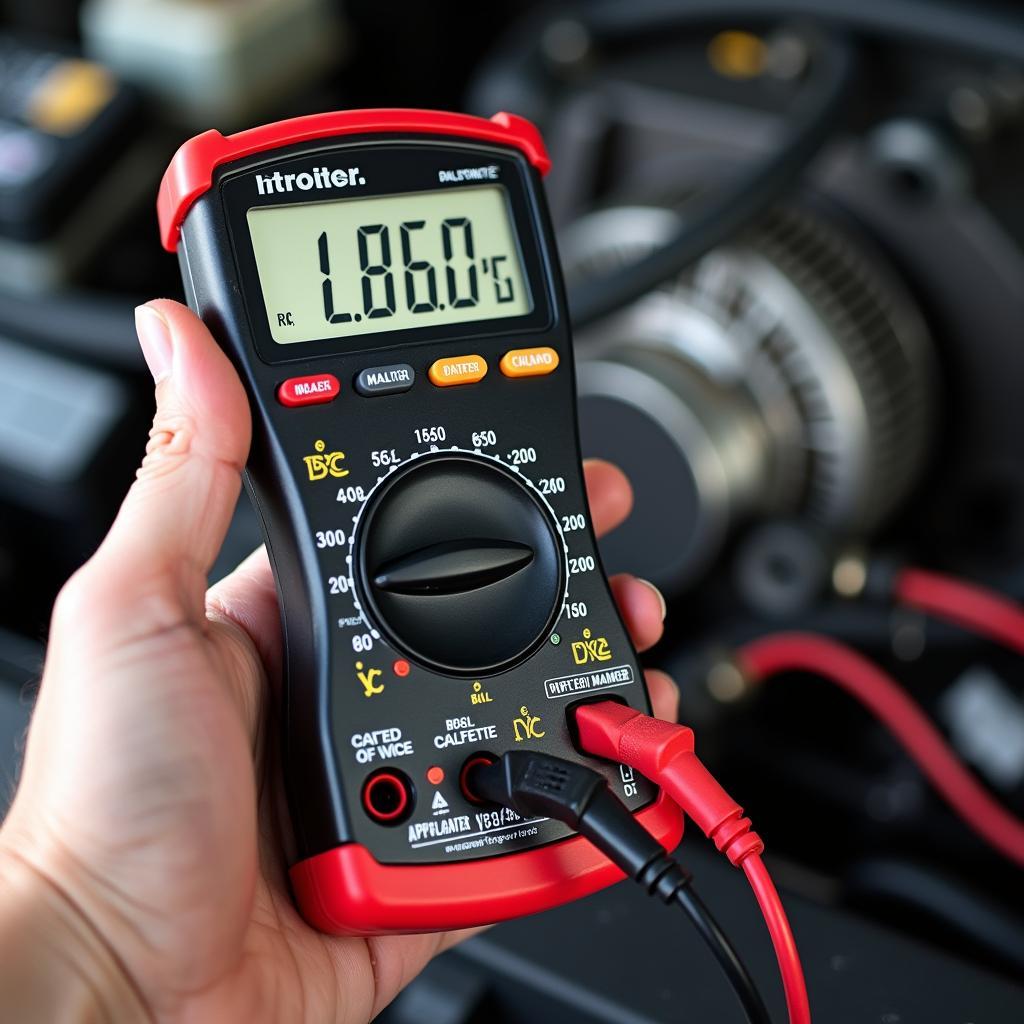 Using a Multimeter to Test Alternator Output
Using a Multimeter to Test Alternator Output
Common Alternator Problems
Here are some of the most common problems that can affect your car alternator:
- Faulty bearings: Bearings within the alternator can wear out, causing noise and eventually leading to a complete failure.
- Damaged diodes: Diodes are crucial components that regulate the flow of electrical current within the alternator. If a diode fails, it can prevent the alternator from charging the battery effectively.
- Burnt stator windings: The stator windings are responsible for generating the electrical current. If they get burnt due to overheating or electrical overload, the alternator will fail to produce electricity.
- Worn brushes: Brushes are small carbon components that make contact with the rotor and transfer electricity. Over time, brushes wear down and can cause intermittent charging problems or a complete failure.
When to Replace Your Alternator
If you suspect that your alternator is failing, it’s best to have it checked by a qualified mechanic. In most cases, replacing the alternator is the only solution to fix a failed unit. You should also replace the alternator if you experience any of the following:
- Excessive noise: If the alternator is making loud noises, such as grinding or whining, it’s a clear sign that it’s nearing failure and should be replaced.
- Intermittent charging problems: If your car battery charges intermittently or the battery light comes on randomly, it’s a good idea to replace the alternator to avoid potential breakdowns.
- Low voltage output: If the alternator’s output voltage is consistently below 13.5 volts, it’s not functioning properly and should be replaced.
Expert Insight
“The best way to avoid alternator problems is to perform regular maintenance on your vehicle. This includes checking the alternator belt, inspecting the wiring, and having the alternator checked by a mechanic during your regular service intervals,” says John Smith, Certified Automotive Technician.
“If you are experiencing signs of a failing alternator, it’s important to address the issue as soon as possible. Ignoring the problem can lead to more serious issues, including a dead battery or a complete breakdown,” adds Jane Doe, Master Automotive Technician.
Conclusion
Understanding the signs of a failing alternator and knowing how to diagnose the problem can save you a lot of trouble and potential breakdowns. If you suspect that your alternator is failing, it’s best to have it checked by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible. By taking the necessary precautions, you can keep your car running smoothly and avoid any unexpected surprises on the road.
Remember: If you have any questions or need assistance, please contact AutoTipPro at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States.
FAQ
- What causes an alternator to fail? Common causes of alternator failure include worn bearings, damaged diodes, burnt stator windings, and worn brushes.
- How long do car alternators last? Alternators typically last for 7-10 years or 100,000-150,000 miles. However, their lifespan can vary depending on factors like driving conditions, maintenance, and environmental factors.
- Can I drive with a failing alternator? It is not recommended to drive with a failing alternator as it can lead to a dead battery, which can leave you stranded. Additionally, a failing alternator can damage other electrical components in your vehicle.
- How much does it cost to replace an alternator? The cost of replacing an alternator can vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle and the labor costs in your area. However, expect to pay anywhere from $200 to $600 or more.
- How do I know if my alternator is charging? You can check if your alternator is charging by measuring the voltage at the battery terminals with the engine running. A healthy alternator should produce a voltage of 13.5-14.5 volts.
- Is it safe to replace an alternator myself? While replacing an alternator is a challenging task, it is possible with the right tools and knowledge. However, it is recommended to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic if you are not comfortable performing the repair yourself.
- What happens if my alternator completely fails? If your alternator completely fails, your car will eventually stop running. The battery will lose its charge, and you won’t be able to start the engine.




Leave a Reply