Thyro8d, also known as the throttle position sensor (TPS), plays a crucial role in your car’s engine performance. This sensor tells your car’s computer the position of your throttle, enabling the engine to adjust fuel and ignition timing accordingly. In older cars, the Thyro8d sensor can malfunction, leading to various issues that affect driving experience and fuel efficiency. This article will guide you through common Thyro8d problems in old cars, help you identify the root cause of the issue, and provide practical solutions to fix the problem.
Understanding the Thyro8d Sensor
The Thyro8d sensor is a crucial component in your car’s electronic system. It’s responsible for converting the position of your throttle (the pedal you press to control engine speed) into an electrical signal that the engine control module (ECM) uses to regulate engine functions.
A malfunctioning Thyro8d can cause various problems, including:
- Rough idling: The engine might idle erratically, stutter, or stall.
- Stalling: The engine may stall when you come to a stop or while accelerating.
- Poor acceleration: The engine may hesitate or struggle to accelerate.
- Increased fuel consumption: The car may use more fuel than usual.
- Check engine light: The “check engine” light may illuminate on your dashboard.
What causes Thyro8d problems in old cars?
Several factors can contribute to Thyro8d problems in old cars:
- Wear and tear: Over time, the sensor’s components can wear out, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and other elements can cause corrosion on the sensor’s electrical connections, hindering proper signal transmission.
- Dirty throttle body: A dirty throttle body can restrict airflow, making it difficult for the sensor to accurately measure throttle position.
- Electrical issues: Faulty wiring or connections in the electrical circuit can also cause problems with the Thyro8d sensor.
Diagnosing Thyro8d Problems
Before diving into repairs, you need to accurately diagnose the issue. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you pinpoint the problem:
- Inspect the Thyro8d sensor: Look for any visible signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Check the throttle body: Ensure the throttle body is clean and free from obstructions. Clean it with a throttle body cleaner if necessary.
- Test the sensor: You can use a multimeter to test the sensor’s voltage output. Compare the readings with the manufacturer’s specifications for your car model.
- Use a diagnostic scanner: A diagnostic scanner can read the ECM codes and provide valuable information about the sensor’s performance.
Repairing Thyro8d Problems
Once you’ve diagnosed the problem, you can proceed with repairs. Here are some common solutions:
- Replacing the Thyro8d sensor: If the sensor is damaged or showing signs of wear and tear, replacing it with a new one is the best solution.
- Cleaning the throttle body: A dirty throttle body can impact the sensor’s performance. Cleaning it with a throttle body cleaner can help resolve the issue.
- Repairing electrical connections: If you find any faulty wiring or loose connections, fix them immediately.
- Consult a mechanic: If you’re not comfortable performing these repairs yourself, consult a qualified mechanic.
Thyro8d sensor replacement: A step-by-step guide
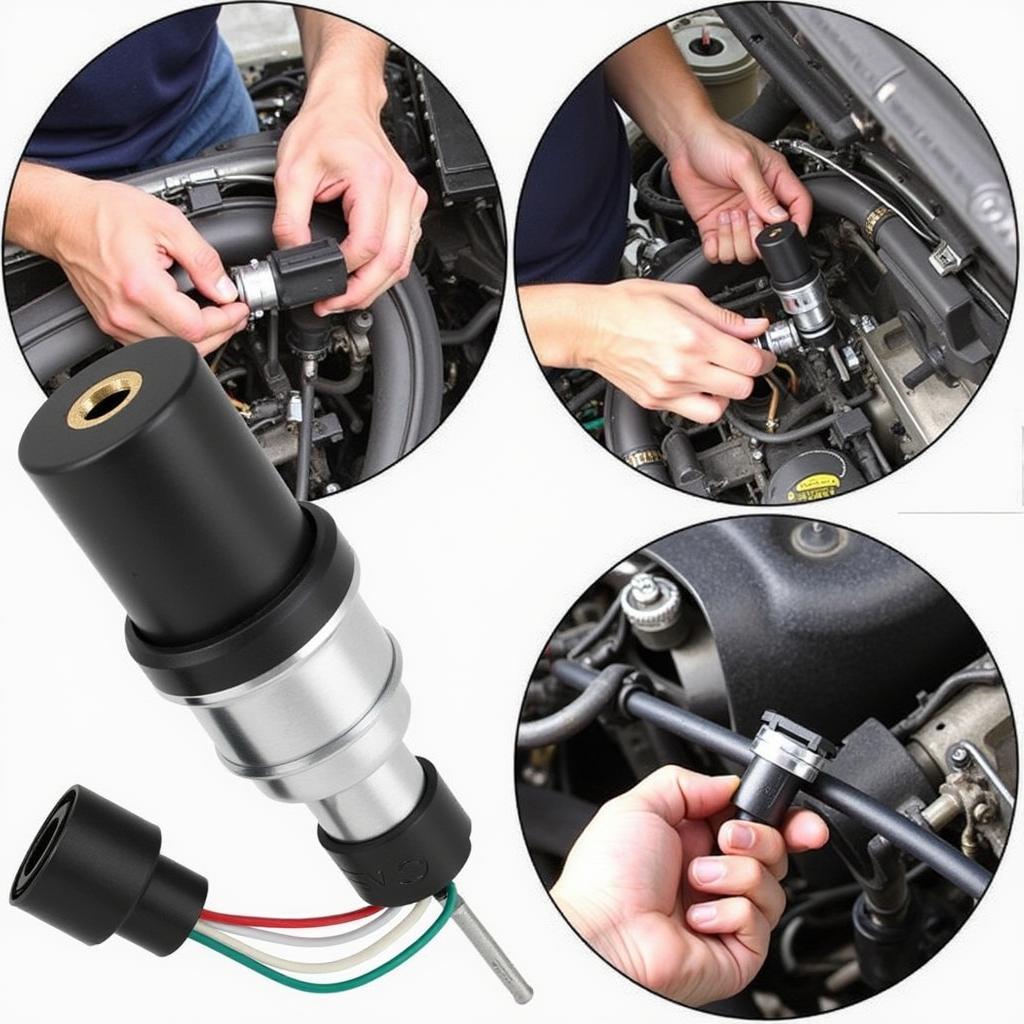 Replacing Thyro8d Sensor
Replacing Thyro8d Sensor
Here’s a step-by-step guide on replacing a Thyro8d sensor:
- Disconnect the battery: To prevent electrical shocks, disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Locate the sensor: Find the Thyro8d sensor on the throttle body. It’s usually attached to the side of the throttle body and has a small electrical connector.
- Disconnect the electrical connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the sensor: Remove the sensor from the throttle body. This may involve removing a few screws or clips.
- Install the new sensor: Install the new sensor in the same location as the old one.
- Connect the electrical connector: Connect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
- Secure the sensor: Secure the sensor to the throttle body using the original screws or clips.
- Reconnect the battery: Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Start the engine: Start the engine and test for any improvement in performance.
Preventive Maintenance
While Thyro8d problems are common in older cars, preventive maintenance can help extend the sensor’s lifespan and prevent issues from arising. Here are some tips:
- Regularly clean the throttle body: Cleaning the throttle body every 30,000 miles or so can help prevent dirt and debris from accumulating and hindering sensor performance.
- Inspect the sensor: During routine maintenance, visually inspect the Thyro8d sensor for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Check electrical connections: Ensure all electrical connections are secure and free from corrosion.
Expert Insights
“As a seasoned mechanic with decades of experience, I’ve encountered countless cases of Thyro8d sensor failures in older cars,” says John Smith, a renowned automotive technician. “The most common culprits are wear and tear, corrosion, and electrical issues. Regularly inspecting and maintaining the sensor can significantly reduce the risk of encountering problems.”
 Thyro8d Sensor Inspection
Thyro8d Sensor Inspection
Conclusion
Thyro8d problems in older cars are common, but they can be effectively diagnosed and repaired. By following the troubleshooting steps and repair guidelines outlined in this article, you can address issues with your Thyro8d sensor and restore your car’s performance. Remember, regular maintenance and inspection can help prevent these problems from occurring in the first place.
For more information and expert assistance, please visit our website or contact us at:
Phone: +1 (641) 206-8880
Office: 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States
FAQ
Q: What are the common symptoms of a faulty Thyro8d sensor?
A: Common symptoms include rough idling, stalling, poor acceleration, increased fuel consumption, and a check engine light.
Q: Can I replace the Thyro8d sensor myself?
A: Yes, you can replace the sensor yourself with the right tools and knowledge. However, if you are unsure, it’s best to consult a mechanic.
Q: How often should I clean the throttle body?
A: It’s recommended to clean the throttle body every 30,000 miles or so. However, you may need to clean it more frequently if you drive in dusty or harsh conditions.
Q: Can a dirty throttle body cause a Thyro8d sensor problem?
A: Yes, a dirty throttle body can restrict airflow, making it difficult for the sensor to accurately measure throttle position.
Q: How long does it take to replace a Thyro8d sensor?
A: The time it takes to replace a Thyro8d sensor can vary depending on the make and model of your car. However, it’s typically a relatively simple repair that can be completed within an hour.




Leave a Reply