Understanding car depreciation is crucial for both car owners and those in the automotive industry. This article dives deep into the Exponential Equation For Car Depreciation Word Problems, providing practical examples and expert insights to help you navigate this complex topic.
Decoding Car Depreciation and its Exponential Nature
Car depreciation, the decrease in a vehicle’s value over time, follows an exponential decay pattern. This means the value drops significantly in the initial years and gradually slows down. Mastering the exponential equation for car depreciation word problems allows you to accurately predict a car’s future value, making informed decisions about buying, selling, or leasing.
Why the Exponential Equation Matters
The exponential equation provides a precise method for calculating car depreciation. This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about making smart financial choices. Whether you’re negotiating a car price, considering an extended warranty, or assessing your vehicle’s trade-in value, understanding depreciation is key.
How to Use the Exponential Equation
The standard exponential equation for car depreciation is V = P(1 – r)^t, where:
- V: Represents the future value of the car.
- P: Represents the initial purchase price.
- r: Represents the depreciation rate (expressed as a decimal).
- t: Represents the time in years.
Let’s look at an example. Suppose you bought a car for $30,000, and it depreciates at a rate of 15% per year. What will its value be after 3 years?
V = 30,000 (1 – 0.15)^3
V = 30,000 (0.85)^3
V ≈ $18,423.75
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many people overestimate a car’s future value by using a linear depreciation model. Remember, depreciation is exponential, meaning the largest value drop happens early on.
- Ignoring market fluctuations: External factors like economic conditions and fuel prices can influence depreciation rates.
- Using the wrong depreciation rate: Different car models and brands depreciate at varying rates. Research is essential.
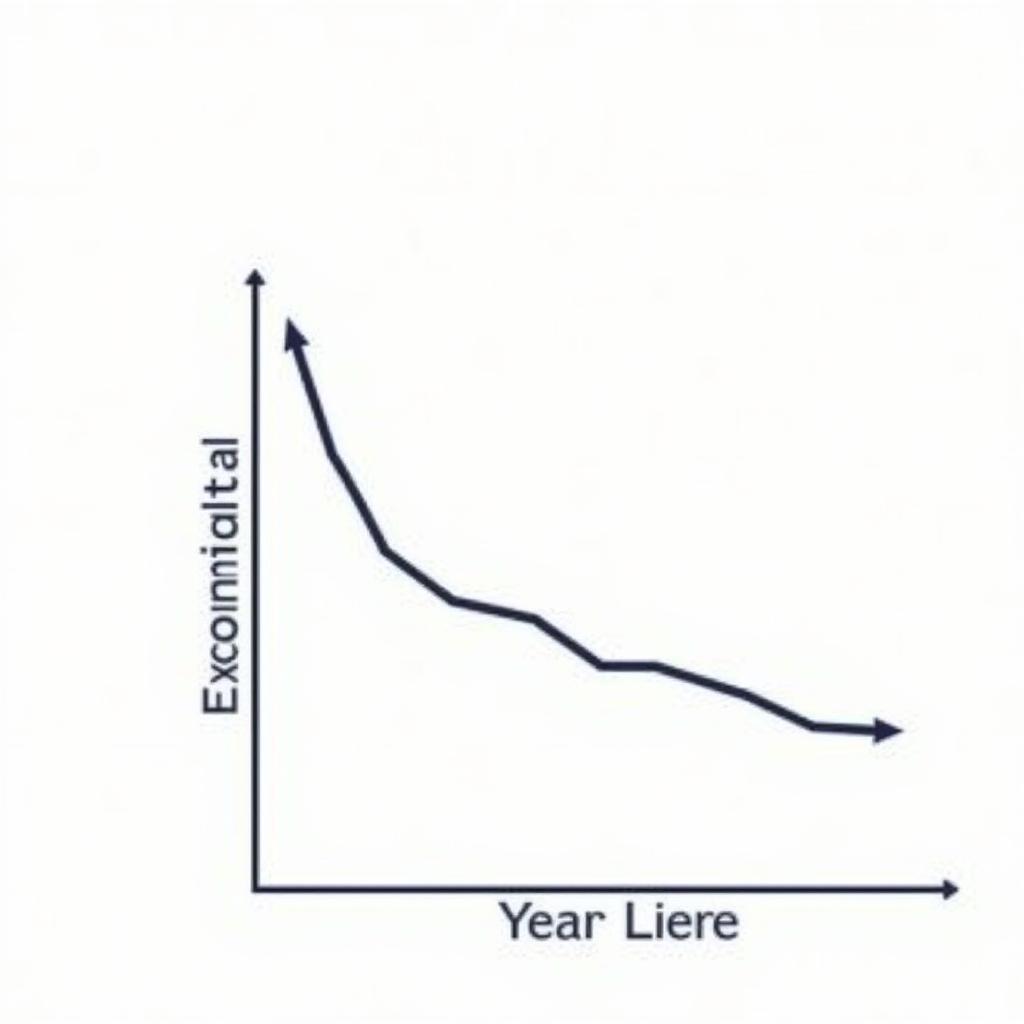 Comparing Linear and Exponential Car Depreciation
Comparing Linear and Exponential Car Depreciation
Real-World Applications of the Exponential Equation
Beyond individual car owners, the exponential equation for car depreciation is valuable for various industry professionals:
- Dealerships: Accurately pricing used cars and offering competitive trade-in values.
- Insurance companies: Determining appropriate insurance premiums and payouts.
- Fleet managers: Optimizing vehicle replacement schedules and managing depreciation costs.
“Understanding the exponential equation for depreciation is not just for mathematicians,” says John Miller, Senior Automotive Analyst at Auto Research Inc. “It’s a practical tool that empowers anyone involved with cars to make informed financial decisions.”
Factors Influencing Depreciation Rate
While the exponential equation provides a framework, several factors influence a car’s depreciation rate:
- Make and model: Luxury cars often depreciate faster than more affordable models.
- Mileage: Higher mileage generally leads to greater depreciation.
- Condition: Well-maintained cars hold their value better.
- Market demand: Popular models tend to depreciate less.
Exponential Equation for Car Depreciation: The Bottom Line
The exponential equation for car depreciation is a powerful tool for navigating the automotive world. Whether you are buying, selling, or simply managing your vehicle’s value, understanding this equation is essential.
“Depreciation is a fact of car ownership,” adds Sarah Johnson, a Certified Automotive Technician. “By understanding the exponential nature of this decline, you can make smart choices and minimize financial losses.”
For further assistance and expert advice, connect with us at AutoTipPro. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States.
FAQ
- What is the simplest way to estimate car depreciation? Use the exponential equation, V = P(1 – r)^t.
- Why does my car lose value so quickly in the first few years? Car depreciation follows an exponential decay pattern, with the steepest decline occurring initially.
- How can I minimize my car’s depreciation? Regular maintenance, low mileage, and choosing a popular model can help.
- Where can I find reliable car depreciation data? Online resources like Kelley Blue Book and Edmunds provide valuable information.
- Does the exponential equation account for all depreciation factors? While it provides a strong foundation, external factors can also influence depreciation.
- How do car dealers use the exponential equation? Dealerships utilize the equation to determine fair prices for used cars and trade-in values.
- Is there a linear equation for car depreciation? No, car depreciation follows an exponential, not linear, pattern.






Leave a Reply