Fuel is the lifeblood of your car, and any issues related to it can significantly impact your vehicle’s performance and overall health. From fuel efficiency problems to engine misfires, understanding common fuel-related car problems is crucial for any car owner or mechanic.
This article will delve into the intricacies of fuel-related car problems, exploring their causes, symptoms, and solutions. We’ll cover everything from the fuel pump to the fuel injectors, providing you with a comprehensive guide to troubleshoot and fix these issues.
Understanding Fuel-Related Car Problems
Fuel-related car problems can manifest in various ways, affecting different aspects of your vehicle’s operation. Understanding these issues requires a basic grasp of how the fuel system works. Here’s a simplified explanation:
- Fuel Tank: The fuel tank stores the fuel.
- Fuel Pump: The fuel pump draws fuel from the tank and sends it to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: The fuel filter removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Lines: Fuel lines transport fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Fuel injectors deliver fuel to the engine cylinders.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The ECU manages the fuel delivery system, controlling factors like fuel pressure and injection timing.
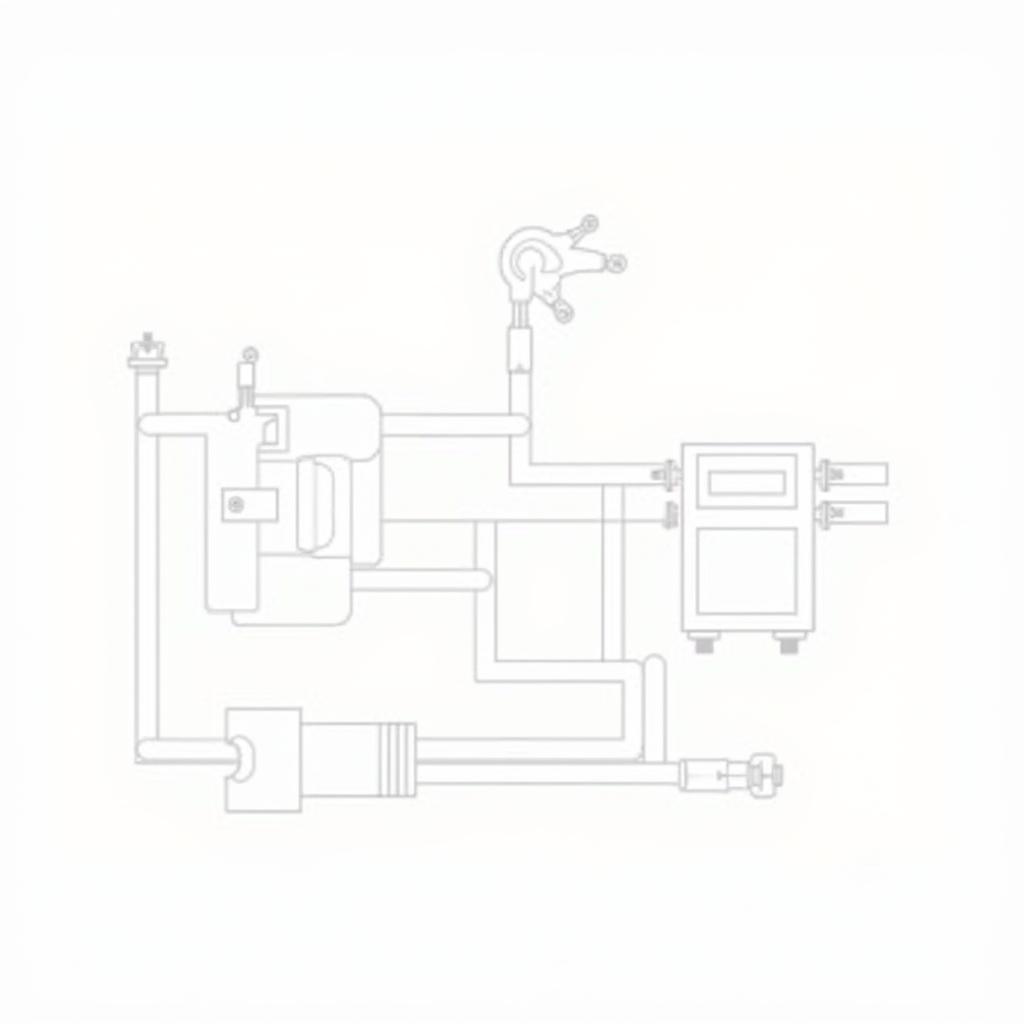 Car Fuel System Diagram
Car Fuel System Diagram
Common Fuel-Related Car Problems and Solutions
1. Engine Stalling or Hesitation
Cause: This issue can be caused by a variety of factors related to the fuel system, such as:
- Clogged Fuel Filter: A clogged fuel filter restricts fuel flow, leading to engine stalling or hesitation, especially when accelerating.
- Faulty Fuel Pump: A failing fuel pump may not deliver enough fuel pressure, resulting in engine stalling or hesitation.
- Dirty Fuel Injectors: Clogged fuel injectors can restrict fuel flow, causing the engine to stall or hesitate.
- Bad Fuel: Contaminated or low-quality fuel can cause engine problems, including stalling and hesitation.
Solution:
- Replace the fuel filter: Regularly replacing the fuel filter is essential for preventing fuel-related problems.
- Check the fuel pump: If the fuel pump is faulty, it needs to be replaced.
- Clean or replace fuel injectors: Cleaning or replacing fuel injectors can resolve issues related to fuel flow.
- Use high-quality fuel: Always use high-quality fuel to prevent contamination and ensure optimal engine performance.
2. Decreased Fuel Efficiency
Cause: Poor fuel efficiency can be caused by several factors, including:
- Clogged Air Filter: A clogged air filter restricts airflow, forcing the engine to work harder and consume more fuel.
- Dirty Fuel Injectors: Dirty fuel injectors can lead to inefficient fuel combustion, resulting in decreased fuel efficiency.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The oxygen sensor monitors exhaust gases and helps the ECU adjust fuel delivery. A faulty oxygen sensor can lead to inaccurate fuel-air mixtures, resulting in decreased fuel efficiency.
- Tire Pressure: Underinflated tires increase rolling resistance, which can lower fuel efficiency.
Solution:
- Replace the air filter: Regularly replace the air filter to ensure optimal airflow.
- Clean or replace fuel injectors: Cleaning or replacing fuel injectors can improve fuel efficiency.
- Inspect and replace the oxygen sensor: If the oxygen sensor is faulty, it needs to be replaced.
- Maintain proper tire pressure: Ensure that your tires are inflated to the recommended pressure.
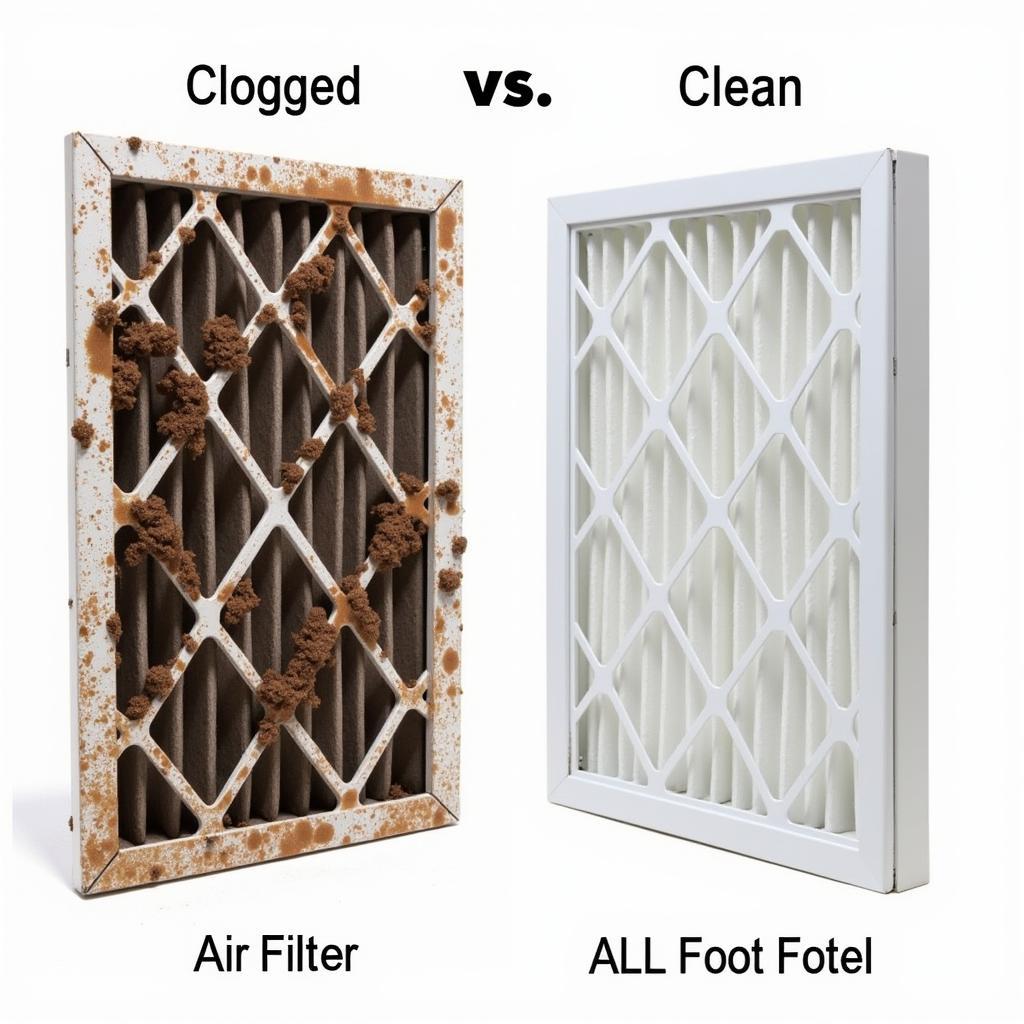 Clogged vs. Clean Air Filter
Clogged vs. Clean Air Filter
3. Engine Misfire
Cause: An engine misfire occurs when one or more cylinders fail to ignite properly, resulting in a rough engine running and reduced power. Some causes include:
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Worn-out or damaged spark plugs can prevent proper ignition, leading to misfires.
- Bad Ignition Coils: The ignition coil delivers electrical current to the spark plugs. A faulty ignition coil can result in misfires.
- Fuel Injector Problems: Fuel injector issues, such as clogging or leakage, can disrupt fuel delivery and cause misfires.
- Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to misfires.
Solution:
- Replace spark plugs: Replacing spark plugs at recommended intervals is crucial for preventing misfires.
- Inspect and replace ignition coils: Check for faulty ignition coils and replace them as needed.
- Clean or replace fuel injectors: Cleaning or replacing fuel injectors can resolve misfires related to fuel delivery.
- Check for vacuum leaks: Inspect hoses and connections for leaks and repair them.
4. Fuel Leaks
Cause: Fuel leaks can be caused by various factors, including:
- Damaged Fuel Lines: Fuel lines can become cracked, corroded, or punctured over time, leading to fuel leaks.
- Faulty Fuel Tank: The fuel tank itself can develop leaks due to rust, damage, or a faulty fuel tank sending unit.
- Loose Fuel Line Connections: Loose connections at the fuel tank, fuel lines, or fuel injectors can cause fuel leaks.
- Faulty Fuel Pump: A faulty fuel pump can leak fuel, especially if the seal is worn or damaged.
Solution:
- Repair or replace fuel lines: Damaged fuel lines need to be repaired or replaced.
- Repair or replace the fuel tank: A leaking fuel tank requires professional repair or replacement.
- Tighten loose connections: Tighten any loose connections to prevent fuel leaks.
- Replace the fuel pump: A leaking fuel pump should be replaced.
5. Fuel Gauge Issues
Cause: Issues with the fuel gauge can be caused by:
- Faulty Fuel Level Sender: The fuel level sender is located in the fuel tank and sends a signal to the instrument panel to display the fuel level. A faulty sender can cause an inaccurate fuel gauge reading.
- Broken Fuel Gauge Wire: A broken or damaged wire connecting the fuel level sender to the instrument panel can lead to an inaccurate or malfunctioning fuel gauge.
- Electrical Problems: Electrical problems in the fuel gauge circuit can also affect the gauge reading.
Solution:
- Replace the fuel level sender: A faulty fuel level sender needs to be replaced.
- Repair or replace the fuel gauge wire: Inspect and repair or replace any broken or damaged fuel gauge wires.
- Diagnose and fix electrical problems: If electrical problems are suspected, have a qualified technician diagnose and repair the issue.
Expert Insights:
“Fuel-related problems can be tricky to diagnose, but understanding the basics of the fuel system and being aware of common symptoms can help you narrow down the issue. If you’re unsure about any of these problems, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic,” says Mr. John Smith, a certified automotive technician with over 20 years of experience.
“It’s also essential to maintain a regular fuel filter replacement schedule and use high-quality fuel to prevent contamination and maintain optimal fuel system performance,” adds Ms. Emily Jones, a renowned automotive engineer specializing in fuel system technologies.
Conclusion:
Fuel-related car problems can significantly impact your vehicle’s performance and can even pose safety hazards. Understanding common fuel-related issues and their causes can help you identify and address these problems promptly.
If you are experiencing any fuel-related issues, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair the problem effectively.
 Mechanic Inspecting Car Engine
Mechanic Inspecting Car Engine
For further assistance or to schedule a consultation, please contact us:
Phone: +1 (641) 206-8880
Office: 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States
FAQs:
- How often should I replace my fuel filter? It is generally recommended to replace your fuel filter every 12,000 to 15,000 miles, or as recommended by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
- Can I use fuel additives to clean my fuel injectors? While fuel additives can sometimes help clean fuel injectors, it’s best to consult with a mechanic before using them.
- What is the best way to prevent fuel-related car problems? Regular maintenance, including replacing the fuel filter, using high-quality fuel, and addressing any fuel leaks promptly, can help prevent fuel-related problems.
- How can I tell if my fuel pump is failing? Symptoms of a failing fuel pump include engine stalling, hesitation, reduced power, and a whining noise coming from the fuel tank.
- What are some signs of a clogged fuel injector? Signs of a clogged fuel injector include decreased fuel efficiency, engine misfires, rough idling, and engine hesitation.






Leave a Reply