A Car Catalytic Converter Problem can manifest in various ways, from a check engine light to decreased fuel efficiency. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and solutions is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and environmental friendliness. This comprehensive guide dives into everything you need to know about catalytic converter issues, offering practical advice for car owners, mechanics, and automotive technicians alike.
What is a Catalytic Converter and Why Does it Matter?
The catalytic converter is a vital component of your vehicle’s exhaust system, responsible for converting harmful pollutants into less harmful substances before they exit the tailpipe. It does this through a chemical reaction facilitated by precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium. A functioning catalytic converter is essential for meeting emission standards and protecting the environment.
Common Car Catalytic Converter Problems
Recognizing the Symptoms
Several signs indicate a potential car catalytic converter problem. These include:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light: This is often the first and most obvious sign. A diagnostic scan can pinpoint the specific code related to the catalytic converter.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: A clogged converter restricts exhaust flow, forcing the engine to work harder and consume more fuel.
- Poor Acceleration: Similar to reduced fuel efficiency, a blocked converter hinders engine performance, leading to sluggish acceleration.
- Rotten Egg Smell: A strong sulfur odor from the exhaust is a classic symptom of a failing catalytic converter. This indicates that hydrogen sulfide isn’t being properly converted.
- Rattling Noise from Under the Vehicle: A broken or damaged internal structure within the converter can cause a rattling sound, especially when accelerating.
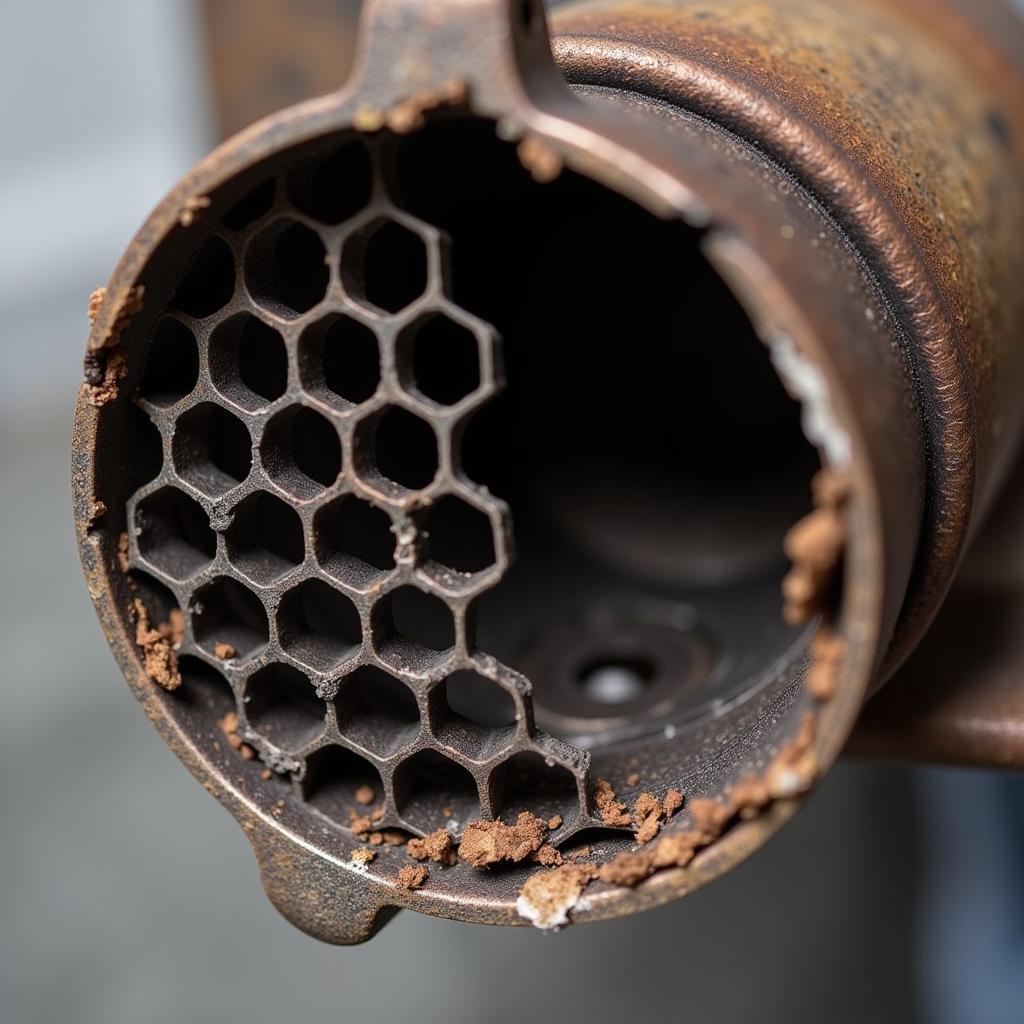 Damaged Catalytic Converter Internal Structure Showing Honeycomb Deterioration
Damaged Catalytic Converter Internal Structure Showing Honeycomb Deterioration
Diagnosing the Issue
Diagnosing a car catalytic converter problem requires a multi-step approach:
- Visual Inspection: Check for physical damage, rust, or signs of overheating on the converter and surrounding exhaust components.
- Diagnostic Scan: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve trouble codes related to the catalytic converter. These codes provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem.
- Exhaust Back Pressure Test: This test measures the pressure in the exhaust system to identify blockages, including a clogged converter.
- Temperature Check: Use an infrared thermometer to measure the temperature of the converter. A significantly higher temperature than normal can indicate a blockage.
What Causes Car Catalytic Converter Problems?
Understanding the root causes can help prevent future issues:
- Engine Misfires: Unburnt fuel entering the converter can overheat and damage the internal components.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: Incorrect readings from oxygen sensors can lead to an improper air-fuel mixture, affecting the converter’s efficiency.
- Leaded Fuel: Using leaded fuel in a vehicle designed for unleaded fuel can quickly poison the catalytic converter.
- Physical Damage: Impacts from road debris or accidents can damage the converter’s external casing or internal structure.
- High Mileage: Over time, the catalytic converter’s internal components can degrade, leading to reduced efficiency.
“Ignoring a failing catalytic converter can lead to more extensive and costly repairs down the road,” advises Robert Miller, a seasoned automotive engineer with over 20 years of experience. “Regular maintenance and timely diagnosis are key to avoiding major headaches.”
Car Catalytic Converter Repair and Replacement
Depending on the severity of the damage, you may need to repair or replace the converter.
- Repair: In some cases, minor damage can be repaired. However, complete replacement is often the most effective solution.
- Replacement: Replacing a catalytic converter can be expensive due to the precious metals used in its construction. Ensure you choose a quality replacement part that meets emission standards. Aftermarket converters are available, but be sure they are compliant with your vehicle’s specifications.
How to Prevent Car Catalytic Converter Problems
Preventative measures can significantly extend the lifespan of your catalytic converter:
- Address Engine Issues Promptly: Fix misfires, oil leaks, and other engine problems as soon as they arise.
- Regular Maintenance: Follow your vehicle’s recommended maintenance schedule, including regular tune-ups and oil changes.
- Use the Correct Fuel: Always use the type of fuel recommended by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
- Avoid Driving Over Obstacles: Be mindful of road debris and avoid driving over rough terrain that could damage the converter.
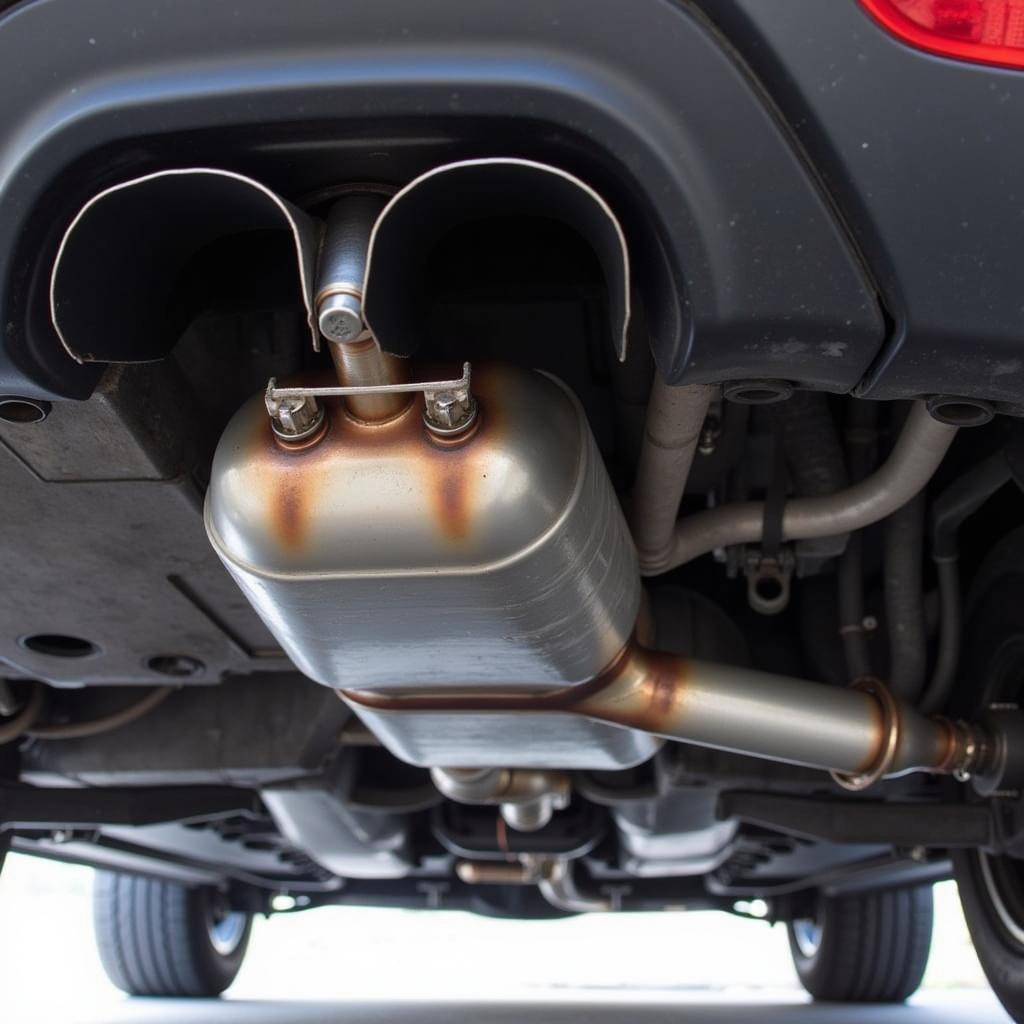 New Catalytic Converter Installation
New Catalytic Converter Installation
“Regular maintenance and a proactive approach to addressing engine issues can go a long way in preventing catalytic converter problems,” states Sarah Chen, a leading expert in automotive emissions control. “This not only saves you money but also helps protect the environment.”
Conclusion
A car catalytic converter problem can significantly impact your vehicle’s performance and contribute to environmental pollution. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and solutions, you can take the necessary steps to maintain a healthy and efficient catalytic converter. If you’re experiencing any of the signs mentioned above, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Connect with AutoTipPro at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States, for expert advice and assistance with your car catalytic converter problem.
FAQ
- How long does a catalytic converter last? Typically, a catalytic converter lasts around 100,000 miles, but this can vary depending on driving habits and vehicle maintenance.
- How much does it cost to replace a catalytic converter? The cost can range from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars, depending on the vehicle make and model.
- Can I drive with a bad catalytic converter? While you might be able to drive for a short period, it’s not recommended as it can lead to further engine damage and increased emissions.
- How can I tell if my catalytic converter is clogged? Symptoms like reduced fuel efficiency, poor acceleration, and a rotten egg smell are indicators of a potentially clogged converter.
- Can a faulty oxygen sensor damage the catalytic converter? Yes, a faulty oxygen sensor can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to overheating and damage to the catalytic converter.
- What are the environmental impacts of a faulty catalytic converter? A faulty converter releases harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and harming the environment.
- How can I prevent catalytic converter theft? Parking in well-lit areas, installing anti-theft devices, and etching your VIN number onto the converter can deter thieves.





Leave a Reply