Car Throttle Mechanical Problems Compilation: a frustrating issue for any driver. From a sticky pedal to complete failure, throttle issues can leave you stranded. This comprehensive guide explores common car throttle mechanical problems, their causes, and how to troubleshoot them.
Understanding the Car Throttle System
Before diving into specific problems, let’s quickly review how the throttle system works. The throttle body controls the amount of air entering the engine. Depressing the gas pedal opens the throttle plate, allowing more air in and increasing engine speed. In older vehicles, this is a purely mechanical linkage. However, modern vehicles often use electronic throttle control (ETC), also known as drive-by-wire.
Common Car Throttle Mechanical Problems
Sticking Throttle
A sticking throttle can be a dangerous situation. This occurs when the throttle plate gets stuck in the open or partially open position. Possible causes include a buildup of carbon deposits, a faulty throttle cable (in older vehicles), or a malfunctioning throttle position sensor (TPS) in ETC systems.
- Carbon Buildup: Carbon deposits can restrict the movement of the throttle plate.
- Faulty Throttle Cable: A frayed or stretched cable can bind, preventing the throttle from returning to its idle position.
- TPS Malfunction: A faulty TPS can send incorrect signals to the engine control unit (ECU), causing the throttle to behave erratically.
Slow Throttle Response
Slow throttle response describes a lag between pressing the gas pedal and the engine reacting. This can be caused by various issues, such as a vacuum leak, a clogged air filter, or problems with the fuel system.
- Vacuum Leak: A leak in the intake manifold can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to sluggish performance.
- Clogged Air Filter: A dirty air filter restricts airflow to the engine, reducing its ability to respond quickly to throttle inputs.
- Fuel System Problems: Low fuel pressure or a clogged fuel filter can also cause slow throttle response.
High Idle Speed
A high idle speed, where the engine revs higher than normal at idle, can indicate a problem with the throttle system, such as a vacuum leak, a faulty idle air control valve (IAC), or a malfunctioning TPS.
- Vacuum Leak: A leak in the intake system can allow unmetered air into the engine, increasing the idle speed.
- Faulty IAC Valve: The IAC valve regulates the airflow at idle. A faulty valve can allow too much air into the engine, causing a high idle.
- Malfunctioning TPS: A faulty TPS can send incorrect signals to the ECU, causing it to maintain a higher than normal idle speed.
Car Throttle Mechanical Problems: Troubleshooting and Repair
Diagnosing throttle problems often requires specialized tools and knowledge. While some basic checks can be performed by car owners, more complex issues should be addressed by qualified mechanics.
- Visual Inspection: Check the throttle cable for fraying or damage (in older vehicles). Look for loose or disconnected vacuum hoses. Inspect the air filter for clogging.
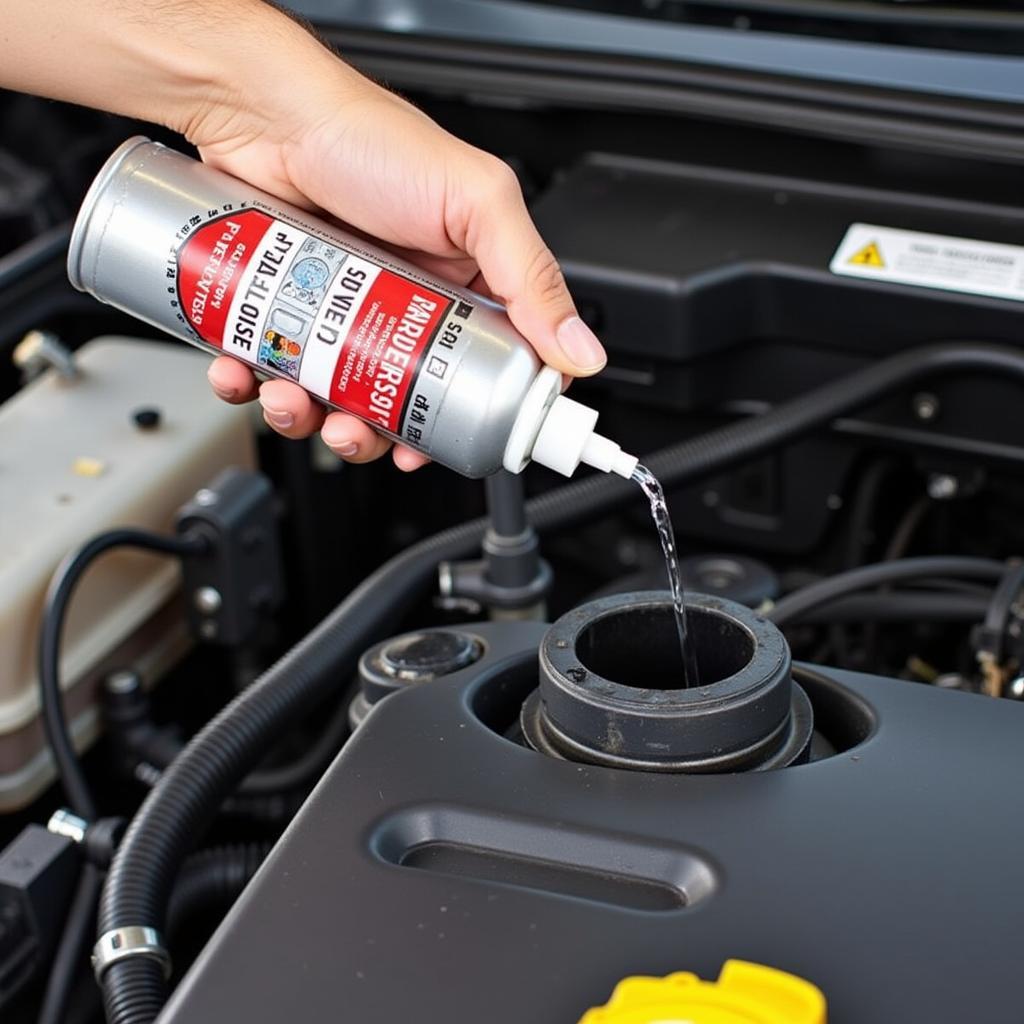
- Throttle Body Cleaning: Cleaning the throttle body with a specialized cleaner can often resolve issues related to carbon buildup.
- Component Replacement: Faulty components, such as the throttle cable, TPS, or IAC valve, will need to be replaced.
“A thorough visual inspection is often the first step in diagnosing throttle problems,” says John Miller, ASE Certified Master Technician. “This can help pinpoint obvious issues like a damaged throttle cable or a disconnected vacuum hose.”
Car Throttle Mechanical Problems Compilation: Drive-By-Wire Systems
Modern vehicles often utilize electronic throttle control (ETC) systems. These systems replace the traditional mechanical linkage with electronic sensors and actuators. While ETC offers improved precision and efficiency, it also introduces potential electronic complexities. Troubleshooting ETC issues requires specialized diagnostic equipment and a deep understanding of the system.
“Drive-by-wire systems can be more complex to diagnose,” explains Sarah Chen, Automotive Electrical Systems Engineer. “Specialized diagnostic tools are often necessary to pinpoint the root cause of the problem.”
Conclusion
Car throttle mechanical problems compilation covers a wide range of issues, from a simple sticking throttle to complex electronic malfunctions. Understanding the underlying causes and knowing how to troubleshoot these problems is essential for maintaining a safe and reliable vehicle. For further assistance or expert advice on car throttle issues, please connect with AutoTipPro at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office located at 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States.
FAQ
- What are the signs of a bad throttle position sensor? Symptoms include rough idling, hesitation or stumbling during acceleration, and a check engine light.
- Can I clean my throttle body myself? Yes, you can clean the throttle body with a specialized cleaner, but be careful not to damage the delicate components.
- How much does it cost to replace a throttle body? The cost varies depending on the make and model of your vehicle but can range from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars.
- What causes a throttle cable to break? Normal wear and tear, corrosion, or improper installation can cause a throttle cable to break.
- How often should I clean my throttle body? It is generally recommended to clean the throttle body every 30,000 to 50,000 miles or as needed.
- Can a bad throttle position sensor cause my car to stall? Yes, a faulty TPS can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, potentially leading to stalling.
- What is the difference between a mechanical and electronic throttle? Mechanical throttles use a cable to connect the gas pedal to the throttle body, while electronic throttles use sensors and actuators to control the throttle electronically.





Leave a Reply