Owning a car with a turbocharger can drastically improve your driving experience, offering increased power and performance. However, like any complex mechanical system, turbochargers are susceptible to problems that can leave you stranded and frustrated. This comprehensive guide delves into the common symptoms, causes, and solutions for Car Turbo Problems, equipping you with the knowledge to address these issues effectively. Whether you’re a car enthusiast, a DIY mechanic, or simply seeking to understand turbocharger problems better, this guide will provide you with valuable insights to keep your turbocharged car running smoothly.
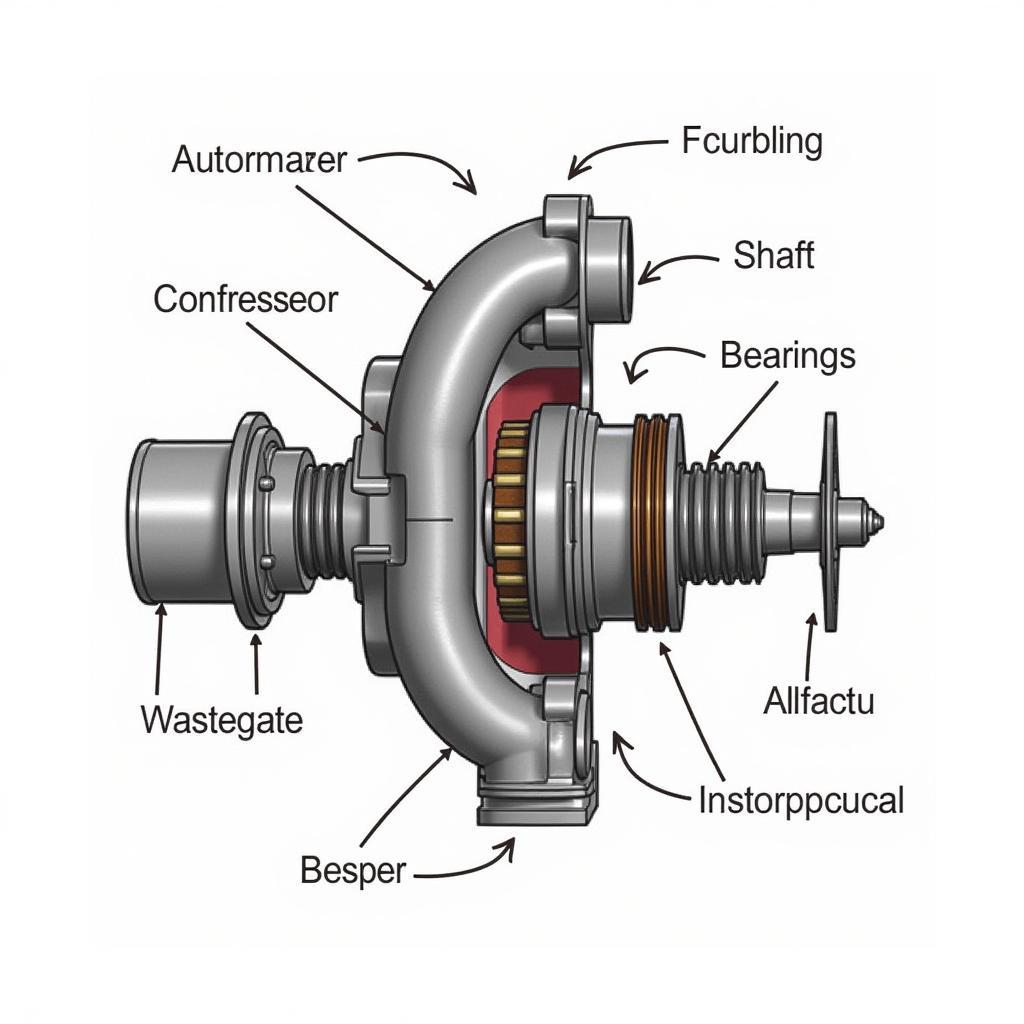 Turbocharger Components
Turbocharger Components
Understanding Your Car’s Turbocharger
Before we dive into the problems, let’s understand how a turbocharger works. In simple terms, a turbocharger is like a powerful fan that forces more air into your engine. This process, called forced induction, allows the engine to burn more fuel and produce more power.
A turbocharger consists of two main components: a turbine and a compressor, connected by a shaft. The engine’s exhaust gases spin the turbine, which in turn drives the compressor. The compressor draws in air, compresses it, and forces it into the engine’s cylinders, resulting in a significant boost in power.
Common Car Turbo Problems and Symptoms
While turbochargers are generally reliable, several issues can arise over time. Recognizing the symptoms early can save you from costly repairs and potential engine damage. Here are some telltale signs of a car turbo problem:
1. Whining or Whistling Noise from the Engine
One of the most noticeable signs of a turbocharger problem is an unusual high-pitched whining or whistling noise coming from the engine, especially during acceleration. This sound often resembles a siren or a dentist’s drill. It’s crucial not to ignore this sound, as it could indicate a problem with the turbocharger bearings or a leak in the intake system.
2. Loss of Power or Reduced Acceleration
A failing turbocharger can’t deliver the same boost pressure, resulting in a noticeable loss of power and sluggish acceleration. You might find it harder to accelerate quickly or maintain speed, especially when going uphill or overtaking.
3. Excessive Exhaust Smoke
Blue smoke from the exhaust usually indicates that the turbocharger is burning oil. This happens when the seals inside the turbocharger wear out, allowing oil to leak into the exhaust stream.
4. Check Engine Light Illumination
Modern cars are equipped with sophisticated engine management systems that can detect turbocharger problems. If the system detects any issues, it will trigger the check engine light on your dashboard.
5. Turbocharger Overboost or Underboost
If the turbocharger is overboosting, it’s delivering more boost than intended, which can lead to engine damage. Conversely, underboosting means the turbocharger isn’t delivering enough boost, resulting in reduced engine power.
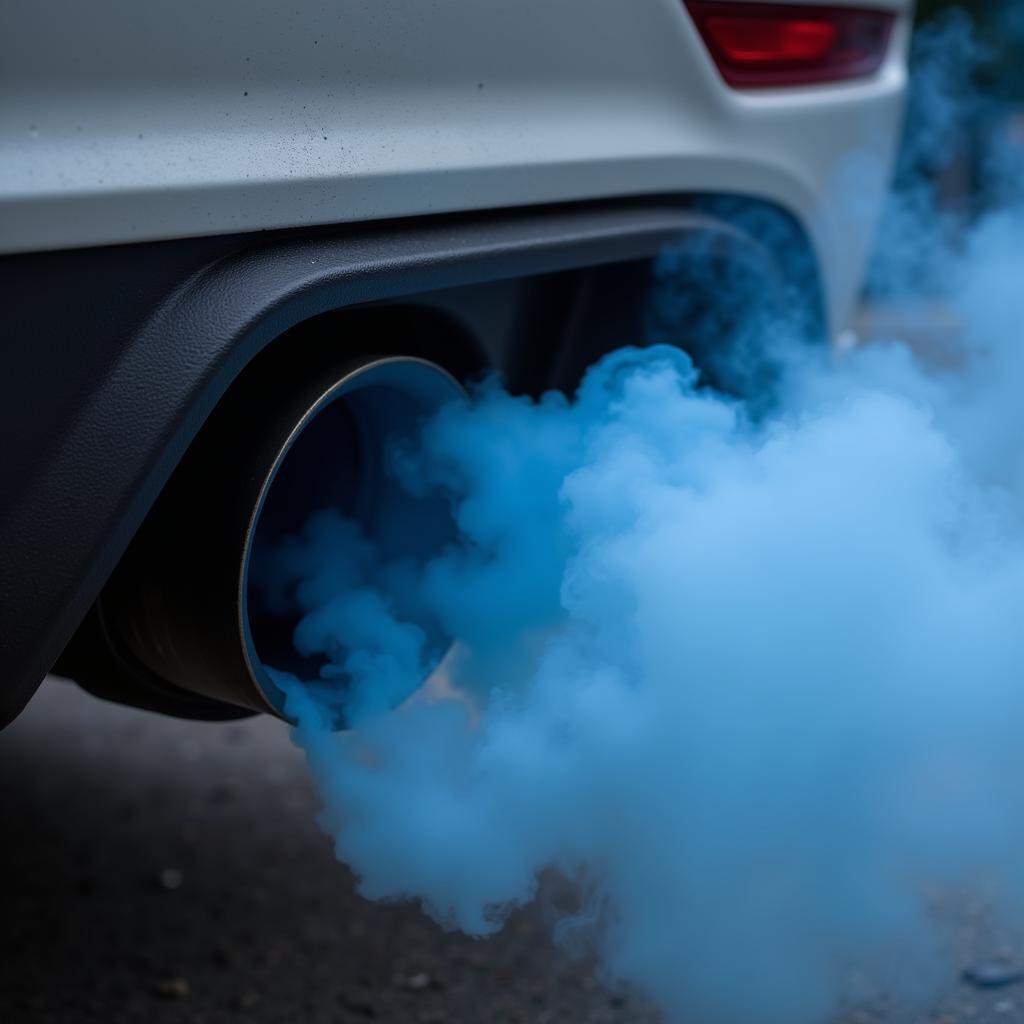 Car with Excessive Exhaust Smoke
Car with Excessive Exhaust Smoke
Common Causes of Car Turbo Problems
Now that you’re familiar with the symptoms let’s explore the common causes behind these car turbo problems:
1. Lack of Lubrication
Like any mechanical component, a turbocharger requires proper lubrication to function correctly. Insufficient oil flow or the use of contaminated oil can lead to premature wear and tear of the turbocharger’s internal components, especially the bearings.
2. Foreign Object Damage
Turbochargers are delicate and susceptible to damage from foreign objects. Even a small piece of debris, such as a loose bolt or a piece of the air filter, can cause significant damage to the turbine blades or compressor wheel.
3. Oil Contamination
Contaminated oil, often caused by infrequent oil changes or a faulty engine, can form sludge and deposits that restrict oil flow to the turbocharger, leading to lubrication problems and potential failure.
4. Overheating
Turbochargers operate at extremely high temperatures, especially during extended periods of high-load driving. Overheating can damage the turbocharger’s internal components, leading to premature wear, oil coking, and potential failure.
5. Faulty Wastegate
The wastegate regulates boost pressure by controlling the flow of exhaust gases that spin the turbine. A malfunctioning wastegate can cause overboost or underboost conditions, negatively impacting engine performance and potentially causing damage.
Diagnosing Car Turbo Problems
If you suspect your car has a turbo problem, it’s crucial to diagnose the issue accurately before attempting any repairs. Here are some steps to help you diagnose the problem:
1. Visual Inspection:
Begin with a visual inspection of the turbocharger and its surrounding components. Look for any signs of oil leaks, loose connections, damaged hoses, or foreign objects around the turbine and compressor.
2. Check for Boost Leaks:
Inspect the intake system for any boost leaks. A boost leak can significantly reduce turbocharger efficiency and performance. You can check for leaks by listening for hissing sounds or using a boost pressure gauge.
3. Inspect the Wastegate:
Check the wastegate actuator arm for smooth movement and make sure it’s connected correctly. A sticking or disconnected actuator arm can cause boost control issues.
4. Oil Analysis:
An oil analysis can reveal valuable information about the condition of your turbocharger and engine. The presence of metal shavings in the oil could indicate severe turbocharger wear.
5. Professional Diagnosis:
If you’re unable to diagnose the problem yourself, it’s best to seek professional help. An experienced mechanic with the right tools and expertise can accurately diagnose the issue and recommend the appropriate repairs.
Solutions for Car Turbo Problems
The solution for a car turbo problem depends on the severity and nature of the issue. Here are some common solutions:
1. Turbocharger Replacement:
In many cases, a complete turbocharger replacement might be necessary, especially if there is significant internal damage to the turbocharger.
2. Turbocharger Rebuild:
If the damage is not extensive, a turbocharger rebuild might be a more cost-effective option. This process involves disassembling the turbocharger, cleaning, inspecting, and replacing worn-out components.
3. Component Replacement:
Sometimes, only specific components, such as the bearings, seals, or the wastegate actuator, might need replacement.
4. Cleaning and Inspection:
If the problem is caught early, a thorough cleaning and inspection of the turbocharger and its related components might be sufficient to restore proper function.
5. Addressing Underlying Issues:
Addressing underlying issues, such as oil contamination, boost leaks, or exhaust restrictions, is crucial to prevent recurring turbocharger problems.
Preventing Car Turbo Problems
Preventing turbocharger problems is always better than dealing with costly repairs. Here are some proactive measures you can take:
1. Regular Oil Changes:
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals. Use high-quality oil that meets the specific requirements of your turbocharged engine.
2. Allow the Engine to Cool Down:
After driving, especially under heavy loads, allow the engine to idle for a minute or two before turning it off. This helps cool down the turbocharger and prevents oil coking.
3. Inspect Air Intake System:
Regularly inspect the air intake system for any leaks, cracks, or blockages. Ensure the air filter is clean and in good condition.
4. Use Quality Fuel:
Use high-quality fuel from reputable sources. Low-quality fuel can cause deposits that restrict exhaust flow and damage the turbocharger.
5. Address Engine Issues Promptly:
Address any engine-related issues, such as oil leaks, excessive oil consumption, or unusual noises, promptly to prevent potential damage to the turbocharger.
Conclusion
Car turbo problems can be frustrating and costly, but understanding the common symptoms, causes, and solutions can help you address them effectively. Remember, early detection and proactive maintenance are crucial for prolonging the life of your turbocharger and ensuring optimal engine performance.
Do you need assistance with a car turbo problem or other automotive issues? Don’t hesitate to reach out to the experts at Autotippro. Our team of experienced technicians is here to provide you with top-notch automotive solutions. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States.
FAQs about Car Turbo Problems
1. How long does a turbocharger last?
With proper maintenance, a turbocharger can last for the lifespan of your car, typically over 100,000 miles. However, factors like driving habits, maintenance practices, and operating conditions can impact its longevity.
2. Can I drive my car with a bad turbo?
While you might technically be able to drive with a bad turbo, it’s not recommended. Driving with a faulty turbocharger can lead to further engine damage and potentially leave you stranded.
3. Is it worth fixing a turbo?
The decision to repair or replace a turbocharger depends on the extent of the damage and the cost of repair. In some cases, a repair might be feasible, while in others, a replacement might be more cost-effective.
4. How can I tell if my wastegate is stuck?
Symptoms of a stuck wastegate include overboost or underboost conditions, unusual noises from the turbocharger, and reduced engine performance.
5. Can a bad turbocharger damage my engine?
Yes, a severely damaged turbocharger can send metal fragments into the engine, causing significant internal damage. It’s crucial to address turbocharger problems promptly to prevent potential engine failure.
Don’t let car turbo problems keep you from enjoying the thrill of the open road. Contact AutoTipPro today for all your turbocharger and automotive needs!





Leave a Reply