A Catalyst Problem In Car can be a frustrating and costly issue. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, diagnosing, and resolving catalyst converter problems, helping car owners, mechanics, and technicians navigate this common automotive challenge.
A failing catalytic converter can severely impact your car’s performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Understanding the signs of a problematic catalytic converter is crucial for timely intervention and preventing further damage. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions regarding repairs and maintenance.
What Causes Catalyst Problems in a Car?
Several factors contribute to catalyst problems. A common culprit is a malfunctioning engine, leading to excessive unburnt fuel entering the converter. This overwhelms the catalyst, causing overheating and damage. Other causes include:
- Leaded fuel: Using leaded fuel in a car designed for unleaded fuel coats the catalyst, rendering it ineffective.
- Faulty oxygen sensors: Inaccurate readings from oxygen sensors disrupt the air-fuel mixture, impacting the converter’s operation.
- Engine misfires: Misfires introduce unburnt fuel into the exhaust system, overloading the catalytic converter.
- Oil leaks: Oil entering the exhaust system contaminates the catalyst, reducing its efficiency.
- Physical damage: Impacts from road debris or accidents can physically damage the converter’s internal structure.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Catalyst Problem
Identifying a failing catalytic converter involves recognizing specific symptoms. These include:
- Reduced engine performance: A clogged converter restricts exhaust flow, leading to sluggish acceleration and decreased power.
- Poor fuel economy: As the converter struggles to function, fuel efficiency drops noticeably.
- Rotten egg smell: A strong sulfurous odor from the exhaust indicates a malfunctioning converter.
- Check engine light: The check engine light illuminates, often accompanied by specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the catalyst.
- Rattling noise from under the vehicle: This noise suggests internal damage to the converter, such as a broken honeycomb structure.
- Overheating catalytic converter: A severely clogged converter can overheat, potentially causing damage to surrounding components.
Similar to car catalytic converter problems, a rattling noise is a strong indicator of internal damage.
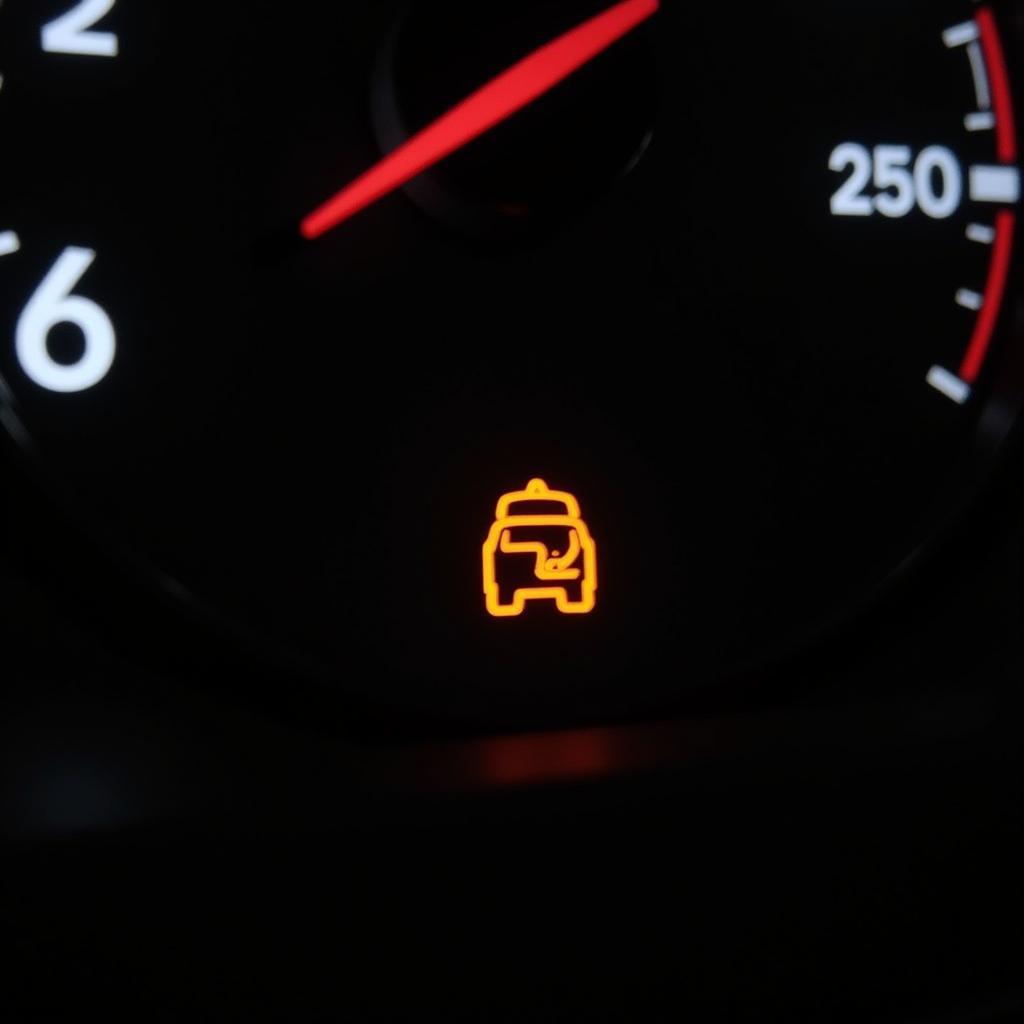 Check Engine Light Illuminated on Car Dashboard
Check Engine Light Illuminated on Car Dashboard
Diagnosing and Fixing Catalyst Problems
Diagnosing catalyst problems requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Visual inspection: Look for signs of physical damage, such as dents or cracks on the converter’s exterior.
- Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs): Use a car problem code reader to retrieve DTCs related to the catalyst system. Understanding these codes can pinpoint the specific issue. Much like interpreting car problem symbols and names, DTCs provide valuable insights into the problem.
- Exhaust back pressure test: This test measures the pressure in the exhaust system, helping identify blockages caused by a clogged converter.
- Emissions testing: This test verifies whether the converter is effectively reducing harmful emissions.
Once diagnosed, the solution often involves replacing the faulty catalytic converter. However, addressing the underlying cause, such as a malfunctioning oxygen sensor or engine misfire, is crucial to prevent recurrence. Sometimes, cleaning the converter might suffice, but replacement is often the most reliable solution.
“Regular maintenance, such as timely oil changes and spark plug replacements, can prevent many catalyst problems,” advises John Smith, Senior Automotive Engineer at Efficient Engines Inc.
Preventing Catalyst Problems: Proactive Maintenance Tips
Preventing catalyst problems is more cost-effective than dealing with repairs. Follow these tips:
- Use the correct fuel type for your vehicle.
- Address engine misfires promptly.
- Regularly check and replace oxygen sensors as needed.
- Fix oil leaks to prevent contamination of the exhaust system.
- Conduct routine maintenance, including oil changes and tune-ups.
“Addressing minor engine issues early can prevent them from escalating into major catalyst problems,” adds Jane Doe, Lead Mechanic at Reliable Auto Repair. This sentiment resonates with those experiencing even seemingly unrelated issues, like what was chevy chases car in modern problems. Preventing these problems can save significant time and money in the long run.
 Pouring the Correct Type of Fuel into a Car’s Gas Tank
Pouring the Correct Type of Fuel into a Car’s Gas Tank
Conclusion
A catalyst problem in car can be a significant issue, but by understanding the causes, symptoms, and solutions, you can effectively address it. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to warning signs are crucial for preventing costly repairs and ensuring optimal vehicle performance. If you’re experiencing catalyst problems or any other car issues, contact AutoTipPro at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States for expert assistance. We are dedicated to providing reliable solutions for all your automotive needs.





Leave a Reply