Car T-cell therapy is a groundbreaking cancer treatment with the potential to send certain cancers into remission. It involves genetically modifying a patient’s own immune cells (T cells) to recognize and attack cancer cells. While this innovative approach has shown remarkable success, there are still some current problems with car T-cell therapy that patients, mechanics, and technicians should be aware of.
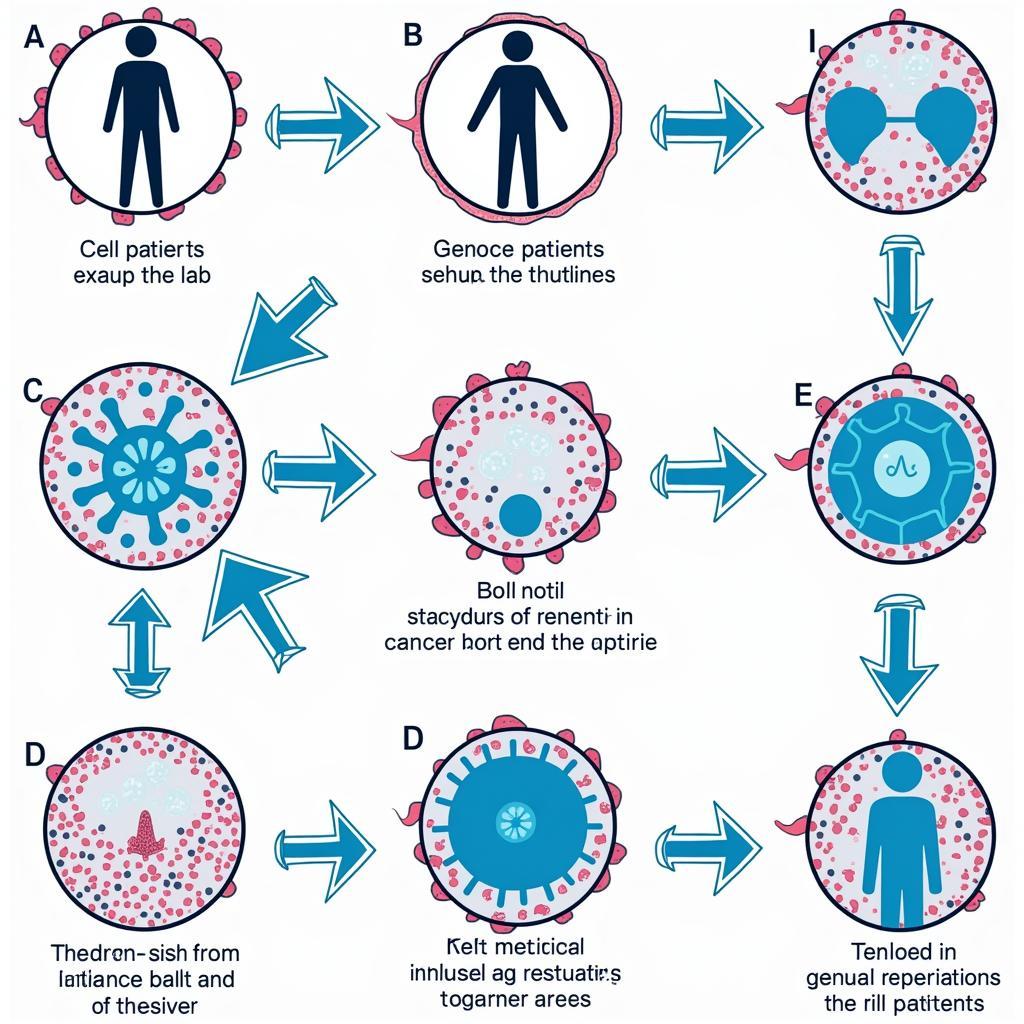 Car T-Cell Therapy Process
Car T-Cell Therapy Process
Understanding the Challenges of Car T-Cell Therapy
As with any new medical technology, car T-cell therapy is not without its limitations. Recognizing these challenges is crucial for managing expectations and improving future treatments.
1. Side Effects and Toxicity
Car T-cell therapy can cause a range of side effects, some of which can be severe.
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): This is one of the most common and potentially serious side effects. It occurs when the engineered T cells rapidly multiply and release large amounts of inflammatory cytokines into the bloodstream, causing flu-like symptoms, low blood pressure, and even organ damage in severe cases.
- Neurological Toxicity: Some patients experience neurological side effects such as confusion, seizures, and difficulty speaking. The exact cause of these side effects is not fully understood but is thought to be related to the inflammatory response triggered by the therapy.
- Prolonged Cytopenia: Car T-cell therapy can suppress the bone marrow’s ability to produce blood cells, leading to low blood counts (cytopenia). This can increase the risk of infections, bleeding, and fatigue.
 Managing Side Effects of Car T-Cell Therapy
Managing Side Effects of Car T-Cell Therapy
While these side effects can be concerning, they are often manageable with close monitoring and supportive care. Medical professionals are continually developing strategies to minimize and treat these side effects, making the therapy safer over time.
2. Relapse and Treatment Resistance
Although car T-cell therapy has led to long-term remission in some patients, relapse remains a significant challenge.
- Antigen Loss: Cancer cells can evolve and lose the specific antigen that the engineered T cells are designed to target. This allows the cancer to evade the immune system’s attack and continue to grow.
- T-cell Exhaustion: Over time, the engineered T cells may become exhausted and less effective at killing cancer cells. This can be due to factors within the tumor microenvironment that suppress immune activity.
Researchers are actively exploring ways to overcome these challenges, such as developing car T cells that target multiple antigens on cancer cells and engineering T cells with enhanced persistence and resistance to exhaustion.
3. Cost and Accessibility
Car T-cell therapy is a complex and personalized treatment that requires specialized facilities and expertise. This complexity contributes to the high cost of the therapy, making it inaccessible to many patients.
Addressing the cost and accessibility issues is crucial for ensuring that this life-saving treatment reaches all those who could benefit from it. Increased research funding, streamlined manufacturing processes, and innovative payment models are all potential solutions.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Car T-Cell Therapy
Despite the current problems, car T-cell therapy remains a promising treatment option for certain cancers. Ongoing research and clinical trials continue to refine the technology and expand its applications.
Some of the exciting developments in the field include:
- Universal Car T Cells: Researchers are developing “off-the-shelf” car T cells that could be used to treat a wider range of patients without the need for individual genetic modification.
- Combination Therapies: Combining car T-cell therapy with other cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy, may enhance its effectiveness and reduce the risk of relapse.
- Improved Safety and Efficacy: Ongoing efforts are focused on developing more targeted and controllable car T cells that minimize side effects and improve long-term outcomes.
Conclusion
Car T-cell therapy represents a significant advancement in cancer treatment, offering new hope for patients with previously limited options. While challenges remain, ongoing research and clinical advancements are paving the way for safer, more effective, and accessible treatments in the future. As we continue to explore the potential of car T-cell therapy, we move closer to a future where more lives are touched and more cancers are cured.
For expert advice and support regarding car T-cell therapy or other automotive issues, contact AutoTipPro at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States.
Frequently Asked Questions about Car T-Cell Therapy
1. What types of cancer can be treated with car T-cell therapy?
Currently, car T-cell therapy is approved for certain types of leukemia and lymphoma. However, clinical trials are underway to investigate its potential in treating other cancers, including solid tumors.
2. How long does car T-cell therapy take?
The entire process, from cell collection to infusion, can take several weeks. After infusion, patients require close monitoring for side effects.
3. Is car T-cell therapy a cure for cancer?
While car T-cell therapy has led to long-term remission in some patients, it’s not considered a guaranteed cure for cancer. Relapse can occur, and more research is needed to determine its long-term effectiveness.
4. What are the eligibility criteria for car T-cell therapy?
Eligibility criteria vary depending on the specific type of cancer and the clinical trial or treatment protocol. Generally, patients must have relapsed or refractory cancer that has not responded to other treatments.
5. What is the long-term outlook for car T-cell therapy?
Car T-cell therapy is a rapidly evolving field with immense potential. As research progresses and technology improves, we can expect to see even more effective and accessible treatments in the future.






Leave a Reply