Problem 11.004 Railroad Car often refers to electrical system malfunctions within railroad cars, impacting various functions like lighting, HVAC, and door operations. This article dives deep into the common electrical issues plaguing railroad cars designated as “problem 11.004” and provides practical troubleshooting solutions for owners, repair shops, and technicians.
Understanding the “Problem 11.004” Designation
The term “problem 11.004” isn’t a standardized industry code. It likely represents an internal designation used by a specific railroad company or maintenance facility. Therefore, deciphering the exact meaning requires understanding the context of its usage. However, we can explore general electrical issues common in railroad cars and provide troubleshooting steps applicable to various scenarios.
Common Electrical Issues in Railroad Cars and Their Solutions
Railroad cars, due to their constant exposure to harsh environments and vibrations, are prone to a range of electrical problems. Some common issues include:
- Faulty Wiring and Connections: Loose connections, corroded wires, and damaged insulation can lead to intermittent power supply, short circuits, and even fires. Regular inspection and tightening of connections are crucial. Replacing damaged wires and applying protective coatings can prevent future problems.
- Malfunctioning Batteries: Railroad cars rely on batteries for various functions, including starting auxiliary power units and powering emergency lighting. Battery testing and replacement at regular intervals are essential.
- Generator Problems: Generators provide the primary power source for many railroad car systems. Issues with the generator’s voltage regulator, rectifier, or alternator can lead to power fluctuations and system failures. Proper maintenance and timely repairs are vital for reliable generator operation.
- Control System Malfunctions: Modern railroad cars employ sophisticated control systems for various functions. Problems with these systems can disrupt operations and require specialized diagnostic tools.
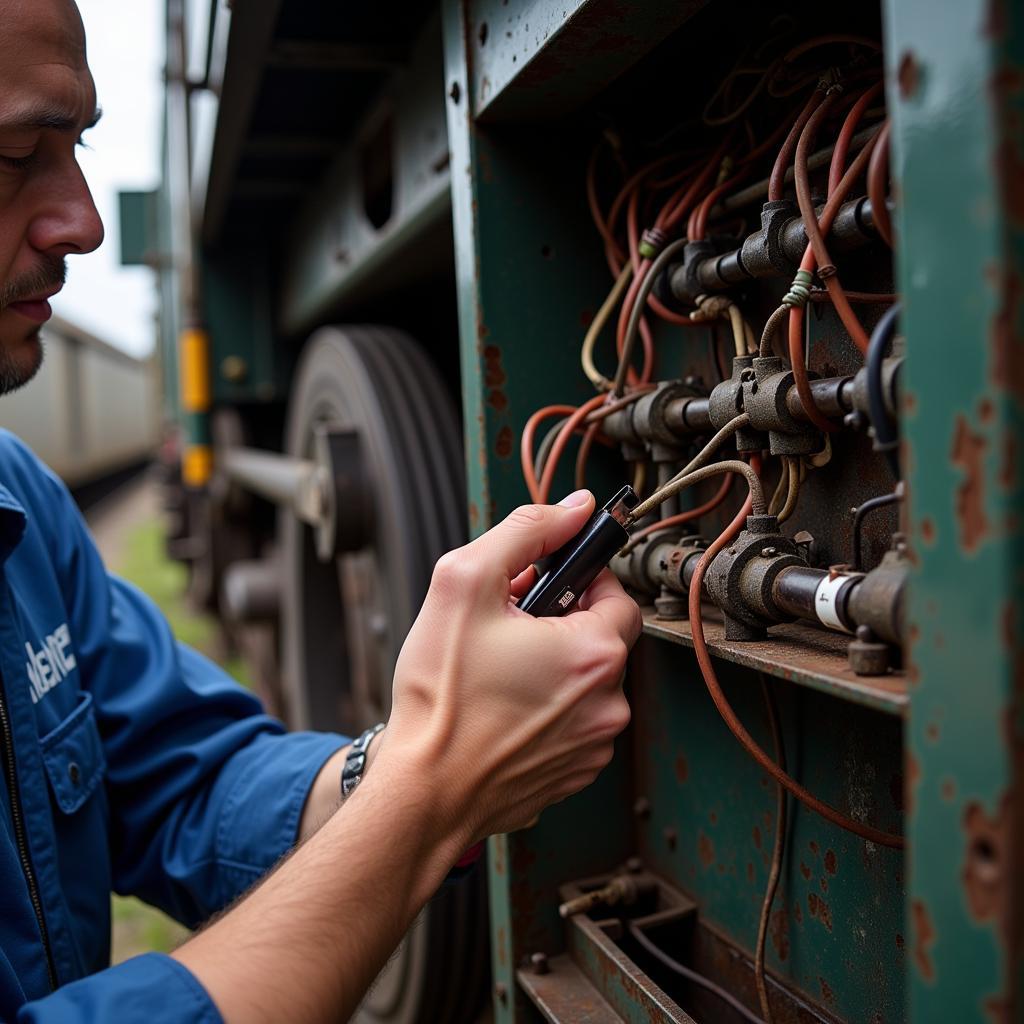 Railroad Car Wiring Inspection
Railroad Car Wiring Inspection
Troubleshooting Electrical Faults: A Step-by-Step Guide
When faced with an electrical issue, a systematic approach is essential. Here’s a step-by-step guide for troubleshooting:
- Identify the Symptoms: Clearly define the problem. Is it a complete power outage, a malfunctioning specific system, or intermittent failures?
- Check the Power Source: Verify the battery voltage and generator output. Ensure all circuit breakers and fuses are functioning correctly.
- Inspect Wiring and Connections: Look for loose connections, corroded wires, and damaged insulation. Pay attention to areas prone to vibration and exposure to the elements.
- Test Components: Use a multimeter to test individual components like relays, solenoids, and sensors.
- Consult Wiring Diagrams: Refer to the railroad car’s specific wiring diagrams to trace circuits and identify potential problem areas.
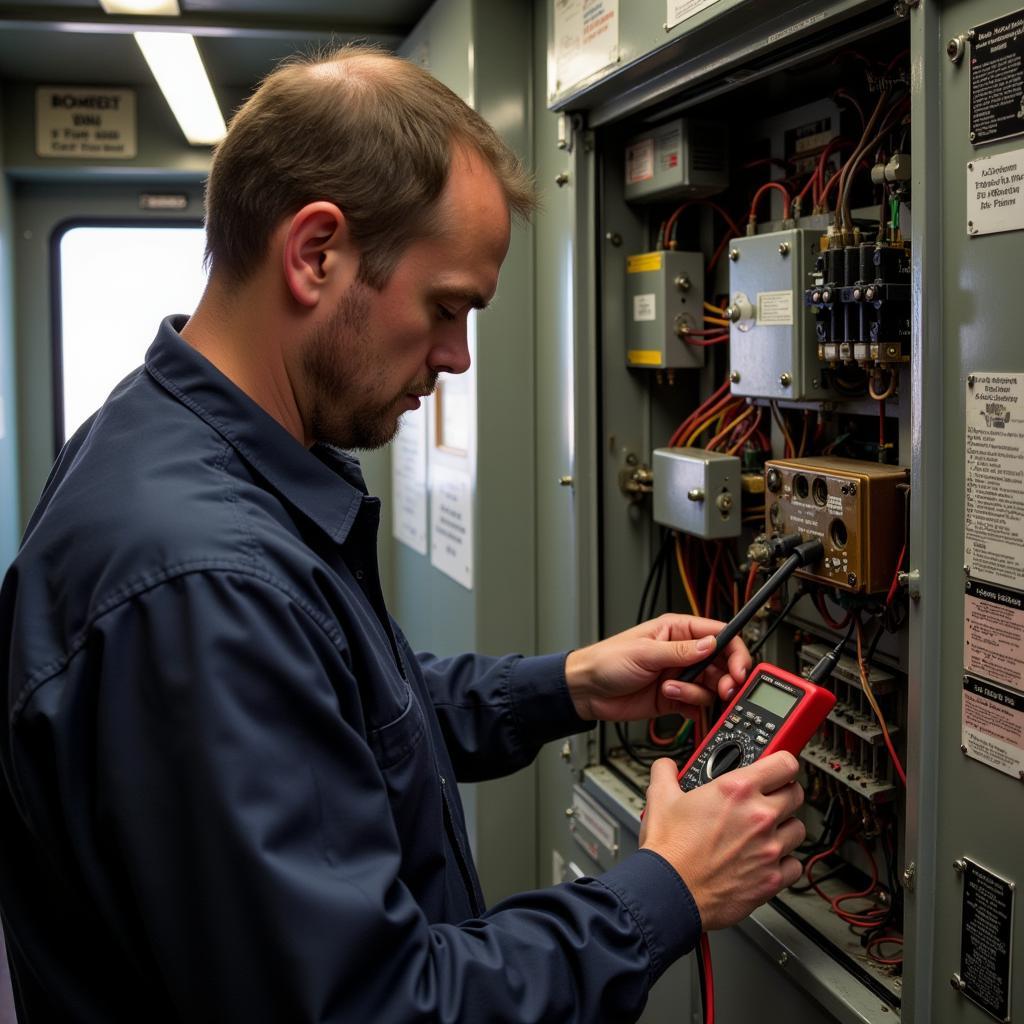 Railroad Car Electrical Testing
Railroad Car Electrical Testing
Advanced Diagnostics and Repair
For complex electrical problems, specialized diagnostic tools and expertise might be necessary. Control system issues often require software diagnostics and specialized equipment.
“Proper grounding is paramount in railroad car electrical systems,” says John Davis, a veteran railroad electrician with over 20 years of experience. “A poor ground can lead to a cascade of electrical problems, making troubleshooting a nightmare.”
Preventative Maintenance: The Key to Reliable Operation
Regular preventative maintenance is crucial for preventing electrical problems and ensuring reliable operation. This includes:
- Visual Inspections: Regularly inspect wiring, connections, and components for signs of damage or wear.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Keep electrical connections clean and lubricated to prevent corrosion.
- Testing and Replacement: Test batteries, generators, and other critical components regularly and replace them as needed.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance and repair activities.
Conclusion: Keeping Your Railroad Cars on Track
Addressing electrical problems in railroad cars, whether labeled “problem 11.004” or otherwise, requires a systematic approach and a good understanding of the electrical systems involved. By following the troubleshooting steps and implementing a robust preventative maintenance program, you can keep your railroad cars running smoothly and minimize downtime. For further assistance or specialized support, connect with Autotippro at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States. We’re here to help you keep your railroad car operations on track.
“Investing in preventative maintenance is always cheaper than dealing with unexpected breakdowns,” advises Sarah Miller, a senior consultant specializing in railroad car maintenance. “A little proactive care can go a long way in preventing costly repairs and downtime.”
FAQ
- What does “problem 11.004 railroad car” mean? It likely refers to an internal code for an electrical malfunction and requires context-specific interpretation.
- What are the most common electrical problems in railroad cars? Faulty wiring, battery issues, and generator problems are frequent culprits.
- How can I troubleshoot electrical problems in a railroad car? Start by identifying symptoms, checking the power source, and inspecting wiring and connections.
- What is the importance of preventative maintenance? It helps prevent problems, extends the lifespan of components, and minimizes downtime.
- Where can I find professional help for railroad car electrical issues? Contact AutoTipPro for expert assistance and support.
- What tools are essential for diagnosing railroad car electrical problems? A multimeter and access to wiring diagrams are crucial.
- How can I prevent corrosion in electrical connections? Regular cleaning and applying dielectric grease can help prevent corrosion.





Leave a Reply