Experiencing electrical issues in your Toyota? A blown fuse might be the culprit. This guide tackles the common “Toyota Car Fuse Problem,” offering practical solutions for car owners, mechanics, and technicians.
A malfunctioning electrical system can be frustrating, and often the root cause is a simple blown fuse. Understanding how to diagnose and fix these problems can save you time and money. After the initial inspection, you may find that other issues, such as those related to a car problems cooling fan, are not the cause of your problems. This article will provide a step-by-step approach to identifying and resolving toyota car fuse problems.
Identifying the Symptoms of a Blown Fuse
How do you know if you’re dealing with a toyota car fuse problem? Look for these telltale signs:
- Sudden malfunction of a specific electrical component: This could be anything from your headlights and radio to your power windows or air conditioning.
- Non-functioning interior lights: If your dome light, map lights, or other interior lights suddenly stop working, a blown fuse is a likely cause.
- A burning smell: A strong, unusual burning smell coming from your dashboard or fuse box could indicate a blown or overloaded fuse. This is a serious issue that should be addressed immediately.
- No power to a specific accessory: If your cigarette lighter, 12V outlet, or other accessories are not receiving power, it could be a fuse issue.
Sometimes seemingly unrelated issues, such as those detailed on our page discussing etios car problems, can actually stem from a simple blown fuse.
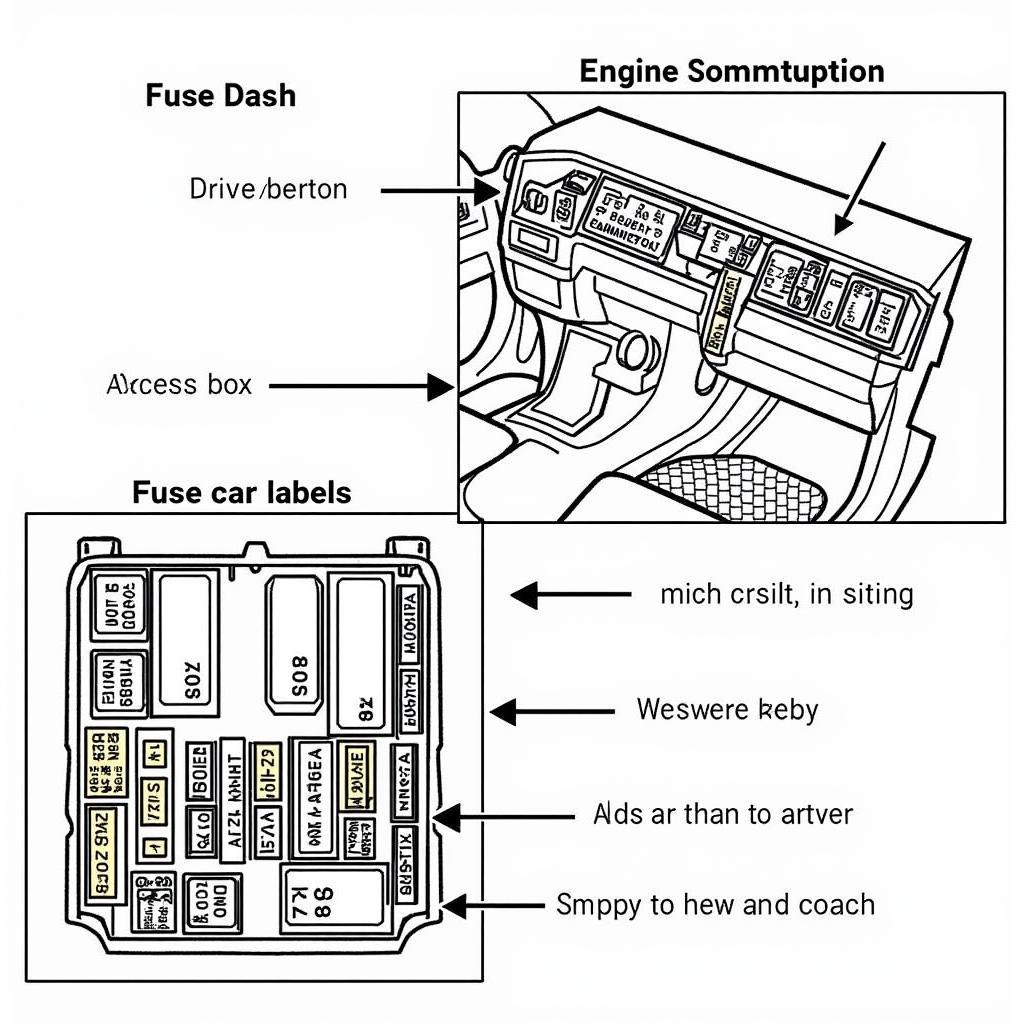 Toyota Car Fuse Box Location
Toyota Car Fuse Box Location
Locating the Fuse Box in Your Toyota
Most Toyotas have two fuse boxes: one under the dashboard on the driver’s side and another in the engine compartment. Consult your owner’s manual for the precise locations in your specific model. The owner’s manual is your best friend when it comes to understanding your car’s electrical system. It will typically contain a diagram of the fuse boxes, showing the location and function of each fuse. Some models, particularly larger SUVs, may even have a third fuse box, often situated in the rear cargo area.
How to Test a Fuse
- Gather the necessary tools: You’ll need a fuse puller (usually found inside the fuse box) or a pair of needle-nose pliers, and a test light or multimeter.
- Identify the suspect fuse: Use your owner’s manual to determine which fuse corresponds to the malfunctioning component.
- Remove the fuse: Carefully pull the fuse straight out using the fuse puller or pliers.
- Inspect the fuse: Look closely at the metal filament inside the fuse. If it’s broken or melted, the fuse is blown.
- Test the fuse (optional): If the filament appears intact, use a test light or multimeter to verify its functionality.
Have you experienced issues with your Toyota Highlander? Our guide on toyota highlander car problems might provide some insightful information.
Replacing a Blown Fuse
Once you’ve identified a blown fuse, replacing it is a simple process:
- Locate the correct replacement fuse: Ensure you use the correct amperage fuse. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can be dangerous and could lead to fire.
- Insert the new fuse: Push the new fuse firmly into the empty slot.
- Test the component: Turn on the ignition and check if the previously malfunctioning component is now working.
“Always use the correct amperage fuse,” advises John Miller, a seasoned automotive electrician. “Using a higher amperage fuse is a fire hazard. It’s like using a garden hose to put out a house fire – it simply won’t work effectively.”
What Causes Fuses to Blow?
Several factors can cause a fuse to blow:
- Short circuits: A short circuit occurs when a positive wire touches a negative wire or ground, causing a surge of current that blows the fuse.
- Overloaded circuits: Plugging too many devices into a single circuit can overload it, causing the fuse to blow.
- Faulty wiring: Damaged or corroded wiring can create resistance, leading to overheating and a blown fuse.
- Faulty electrical components: A malfunctioning component can draw excessive current, blowing the fuse.
Problems after heavy rain? A blown fuse could be a contributing factor. Check our article on car problems after heavy rain for more information.
When to Seek Professional Help
While replacing a blown fuse is a straightforward task, some situations warrant professional help:
- Repeatedly blown fuses: If a fuse blows repeatedly after being replaced, there’s likely an underlying electrical problem that needs to be diagnosed and repaired.
- Difficulty locating the fuse box or identifying the correct fuse: If you’re unsure about which fuse controls the malfunctioning component, it’s best to consult a professional.
- Uncertainty about the cause of the blown fuse: If you suspect a more complex electrical issue, such as a short circuit or faulty wiring, it’s best to leave the diagnosis and repair to a qualified technician.
“Don’t underestimate the complexity of a car’s electrical system,” cautions Sarah Chen, an experienced automotive engineer. “If you’re not comfortable working with electrical components, it’s always best to seek professional help.”
Conclusion
Troubleshooting a toyota car fuse problem can often be handled with a little know-how. This guide has provided the steps and information needed to identify, test, and replace blown fuses. However, remember that persistent fuse problems often signal deeper issues. If you experience recurring blown fuses, contact us at AutoTipPro at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 500 N St Mary’s St, San Antonio, TX 78205, United States.
 Car Fuse Kit with Assorted Fuses
Car Fuse Kit with Assorted Fuses
Having trouble starting your car? Our guide on car start problem sound could be helpful.







Leave a Reply